Freedom in Metal AM Develompent & Production
Steels
Steels are a broad category of iron-based materials known for their exceptional combination of strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. These attributes make steels indispensable in industries such as construction, automotive, machinery, and tooling. Depending on their chemical composition and heat treatment, steels can be tailored for various operating conditions, from high corrosion resistance to hardness needed for heavy mechanical loads. The carbon content and the heat treatment are crucial to adjust the tensile strength and plasticity by formation desired phase composition.
STEELS
Characterization & Properties
Characterization & Properties
Steels are distinguished by several properties that make them widely used in industry. Key characteristics include:
Steels are distinguished by several properties that make them widely used in industry. Key characteristics include:
High Strength and Hardness
Steels can withstand significant loads, making them ideal for structural applications.
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steels are resistant to moisture and chemicals, making them suitable for aggressive environments.
Good Machinability
Steels can undergo various processing methods, such as welding, forging, and machining, making them versatile in application.

CHOOSE YOUR COMPOSITION
Example High-Temperature Metal Compositions
These alloys provide optimal performance in high-stress, high-temperature environments where conventional materials would fail.
01
Nickel-based Superalloys (e.g., Inconel, Hastelloy)
These superalloys are designed to maintain mechanical strength at high temperatures. They are often used in jet engines, gas turbines, and power plants.
02
Cobalt-based Alloys (e.g., Haynes, Stellite)
Known for their excellent thermal and oxidation resistance, cobalt alloys are used in critical components like turbine blades and medical implants where high temperature and wear resistance are essential.
03
Titanium Alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V)
Titanium alloys offer an excellent balance of strength, low weight, and high-temperature resistance. They are frequently used in aerospace applications such as airframes, jet engines, and exhaust systems.
STEELS
Applications
Steels are used in a wide range of industrial applications, including:

METAL POWDES PRODUCTION
Where to Buy Steel Powders?
Steels which are mostly in additive manufacturing are stainless steels and/or tool steels with injection mold as the most common application. However if you are looking for steels with tailored chemical composition to benefit from small grain size obtained in AM or study some unique effects like transformation induced plasticity (TRIP effect) then such steel powders are hardly available.
WHY AMAZEMET
Why Choose AMAZEMET Steel Powders?
AMAZEMET’s steel powders are known for their reliability and consistent quality. Here’s why our powders stand out:
Uniform Particle Size
Using advanced atomization techniques, our powders are processed to consistent particles ideal for precision manufacturing.
Customized Options
We offer custom steel powder compositions tailored to meet specific project requirements.
Proven technology
The atomization methods we use are efficient and ensure the powders are suitable for modern manufacturing techniques like additive manufacturing.
ORDER POWDERS
High-Temperature Metal Powders for Sale
AMAZEMET provides steel powder production services, with powders customizable to specific customer requirements. Production using plasma ultrasonic atomization ensures high purity and uniform particle size, essential for advanced manufacturing processes.
Austenitic steels
are non-magnetic stainless steels with a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure, typically containing high levels of chromium (16–26%) and nickel (6–
22%). They provide excellent corrosion resistance, ductility, and toughness, making them widely used in food processing, chemical industries, and medical equipment.
RAFM Steel (Reduced Activation Ferritic-Martensitic Steel)
are designed for nuclear applications and contain reduced activation elements like chromium (8–10%), tungsten, and vanadium to limit long-term radioactivity. They offer good mechanical strength and thermal stability under high radiation exposure, making them suitable for fusion reactor components.
Bainitic Steel
feature a microstructure of bainite, a combination of ferrite and cementite, formed through controlled cooling. Key elements like carbon, silicon, and manganese contribute to their high strength, toughness, and wear resistance, making them ideal for automotive components, rails, and armor applications.
Tool Steel
are high-performance steels containing elements like carbon, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten, which provide hardness and wear resistance. They are used in cutting, shaping, and forming tools, as well as in molds and dies, due to their ability to maintain strength under extreme conditions.
Maraging Steel
are ultra-high-strength steels characterized by low carbon content and additions of nickel, cobalt, and molybdenum, which undergo age hardening to form martensitic structures. They are used in aerospace, tooling, and high-performance applications requiring exceptional strength and fracture toughness.
TRIP (Transformation-Induced Plasticity) Steels
utilize a retained austenite phase that transforms into martensite under mechanical deformation, enhancing strength and ductility. They typically contain carbon, silicon, and manganese and are widely used in automotive applications for lightweight, high-strength components.
TWIP (Twinning-Induced Plasticity) Steels
exhibit exceptional ductility and energy absorption due to mechanical twinning that occurs during deformation. These steels are rich in manganese (15–30%) and are ideal for applications requiring high formability and impact resistance, such as structural components in crash-resistant vehicles.
FREEDOM IN METAL AM
DEVELOPMENT & PRODUCTION
HIGH QUALITY METAL POWDERS
How to Make Steel Powders?
Creating steel powders involves converting the metal into small, uniform particles suitable for various manufacturing processes. A common method is plasma ultrasonic atomization, which includes the following steps:
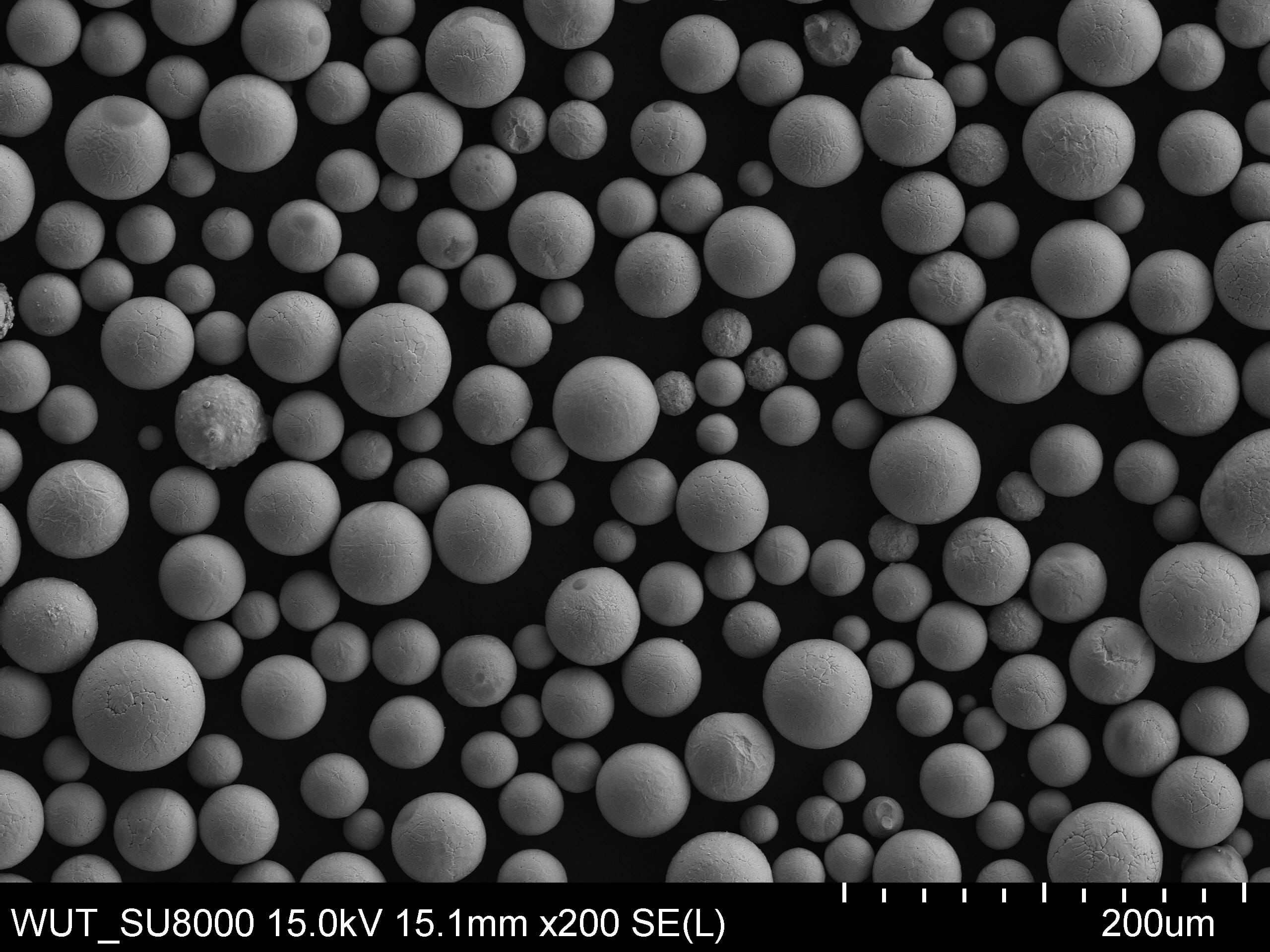

Custom Powders In-House
For companies and research institutions looking to produce their own steel powders, AMAZEMET offers the rePOWDER metal powder atomizer. This system enables in-house production of custom alloy powders, giving full control over the material’s properties.
The benefits of the rePOWDER system include:
- Flexibility: Create steel powders with specific compositions tailored to your project needs.
- Cost Efficiency: In-house powder production reduces reliance on external suppliers.
- Versatility: The system is capable of processing a wide range of steel compositions, ideal for research and small-scale production environments.
- Compact size: The floor space which is required for installation of a rePOWDER ultrasonic atomization platform is almost the same as for a mid-sized metal 3D printer.






