Freedom in Metal AM Develompent & Production
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT
We specialize in turning challenges into opportunities through cutting-edge research and collaborative development. With expertise in advanced materials, ultrasonic atomization and metal additive manufacturing, we partner with leading institutions to pioneer innovative solutions.
CHALLENGES
Identify the Key Barriers to Innovation
The path to innovation is often hindered by common obstacles. These barriers can stall progress and limit the potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
Looking for a reliable partner?
It can be challenging to find a dependable, experienced partner with a proven track record.
Trying to find an industrial partner?
A lack of industrial partnerships may impede efforts to bridge the gap between research and real-world applications.
Seeking effective project leadership?
A shortage of qualified project leaders or fresh perspectives can hinder the development and execution of transformative initiatives.
Need an access to advanced technologies?
Restricted access to cutting-edge technologies or materials can slow innovation and diminish competitive advantage.
Want to secure funding?
Obtaining financial support for ambitious projects often proves difficult, impeding timely progress.

Scientific cooperation
One of the most important challenges facing the development of science and industry is the formation of partnerships that foster interdisciplinary and international cooperation – for example, research project collaborations between companies and universities.
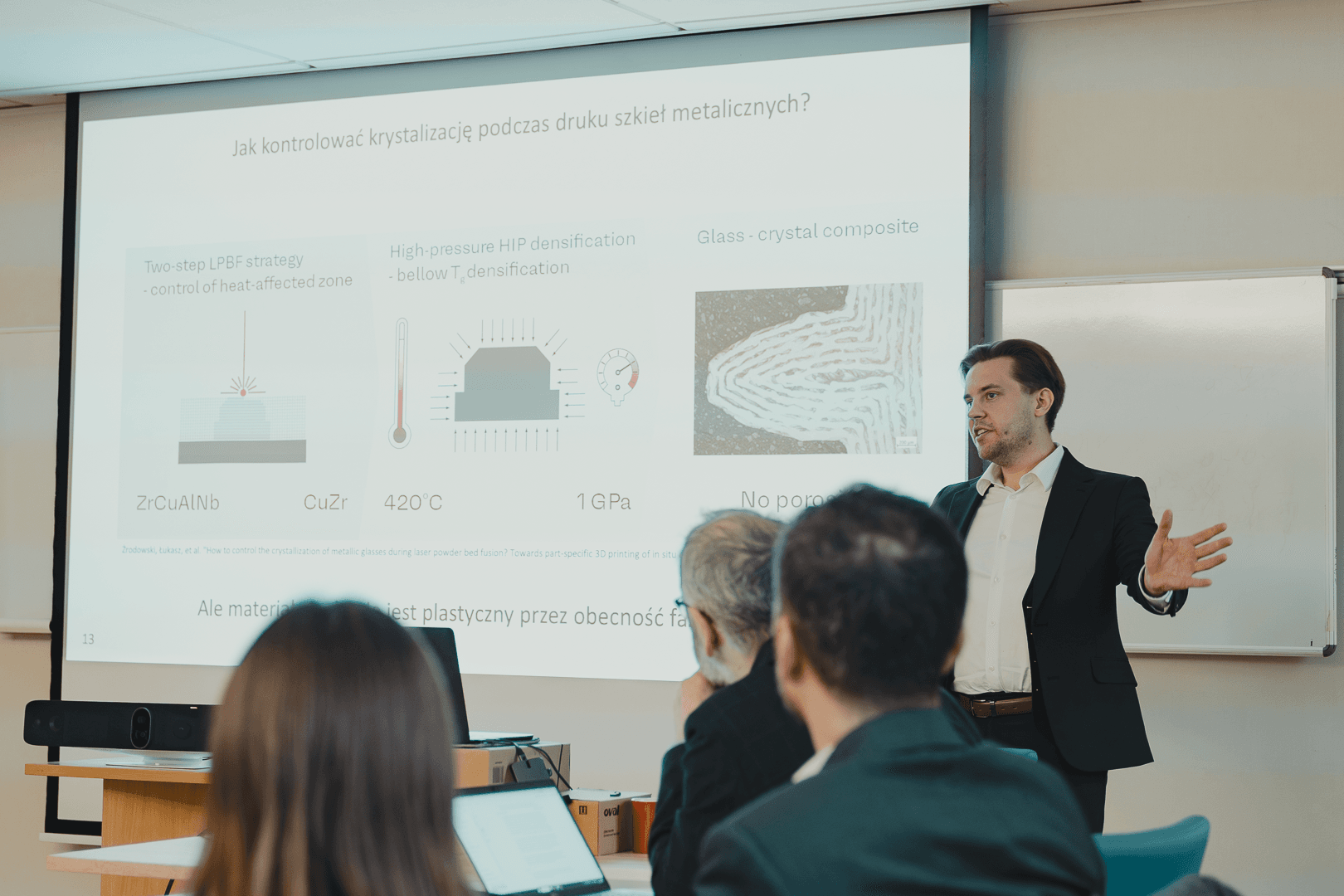
The greatest value for partners who collaborate with AMAZEMET is the scientific support of the Warsaw University of Technology. The specialists involved in these projects have extensive experience in materials engineering, and they understand the need for research and development. Applying these skills while using innovative technologies, such as ultrasonic atomization, makes AMAZEMET a unique contributor to the consortium.
LET’S TALK ABOUT COLLABORATION
The fact that we come from an academic environment has a strong influence on the nature of our business. That is why one of our main areas of interest is scientific cooperation, especially in the framework of scientific and research projects with universities, institutes, scientific and research centers, or R&D departments in private sector.

R&D COLLABORATION
WHAT WE OFFER AS A CONSORTIUM PARTNER
By collaborating with AMAZEMET, you gain a reliable, innovative partner who delivers measurable outcomes. Our expertise and advanced technologies, make us the ideal – both scientific and industrial – consortium partner for research projects. We position ourselves as an active partner, offering tangible intellectual value and commitment. Partnering with us provides access to:
01
Metal Powders and Samples
High-quality materials tailored for research and development.
02
Advanced Machinery
A state-of-the-art facility equipped for innovative projects.
03
Collaborative Opportunities
Co-authoring publications and patents with our team.
04
Technical Consultancy
Expert guidance to navigate complex technical challenges.
05
Recycling Services
Small-scale powder recycling to maximize resource efficiency.
06
Experienced Project Leaders
Dedicated scientists to lead and co-develop innovative solutions.
07
New Technologies and Materials
Development of novel materials for advanced applications, and expertise in ultrasonic atomization.
08
Additive Manufacturing
Metal additive manufacturing capabilities for prototypes and production.
09
Easier Funding Acquisition
Our SME status and strong track record enhance funding opportunities.
FREEDOM IN METAL AM
DEVELOPMENT & PRODUCTION
OUR SCIENTIFIC PARTNERS
By forging strategic alliances with industry-leading organizations, we create an ecosystem that nurtures innovation, broadens market access, and accelerates the realization of cutting-edge solutions. Each of our partners brings a unique blend of expertise, resources, and networks that help overcome critical obstacles.












GROWING LIST OF PUBLICATIONS
In AMAZEMET we are committed to the dissemination of groundbreaking research in advanced materials, metallurgical engineering and additive manufacturing. Our publications include scholarly articles that delve deep into a range of topics and offers unique insights into cutting-edge methodologies. We take pride in fueling the curiosity of researchers and practitioners alike, fostering an environment conducive to learning, discovery, and the broadening of intellectual horizons.
Authors: Mohammad Pourshams; Hediyeh Dabbaghi; Behrang Poorganji; Mohammad Elahinia
Authors: Mohammad Pourshams; Hediyeh Dabbaghi; Behrang Poorganji; Mohammad Elahinia
Authors: Mohammad Pourshams; Hediyeh Dabbaghi; Behrang Poorganji; Mohammad Elahinia
Authors: Mohammad Pourshams; Hediyeh Dabbaghi; Behrang Poorganji; Mohammad Elahinia
OUR CUSTOMERS
Our customers lie at the heart of everything we do, driving us to constantly refine our offerings and deliver exceptional value. Through this client-focused approach, we help unlock opportunities, shape meaningful advancements, and ensure that our work consistently meets—and often exceeds—their expectations.

Join forces with AMAZEMET
Invite Us to Your Consortium
By collaborating with AMAZEMET, you gain a reliable, innovative partner who delivers measurable outcomes. Our expertise and advanced technologies, make us the ideal – both scientific and industrial – consortium partner for research projects. We position ourselves as an active partner, offering tangible intellectual value and commitment.
MEET OUR TEAM

Łukasz Żrodowski
CEO, co-founder, inventor

Adrian Truszkowski
Sales Director

Bogdan Dąbrowski
Sales Manager

Jakub Ciftci
Application Engineer

Tomasz Choma
Application Engineer

Bartosz Morończyk
Application Engineer