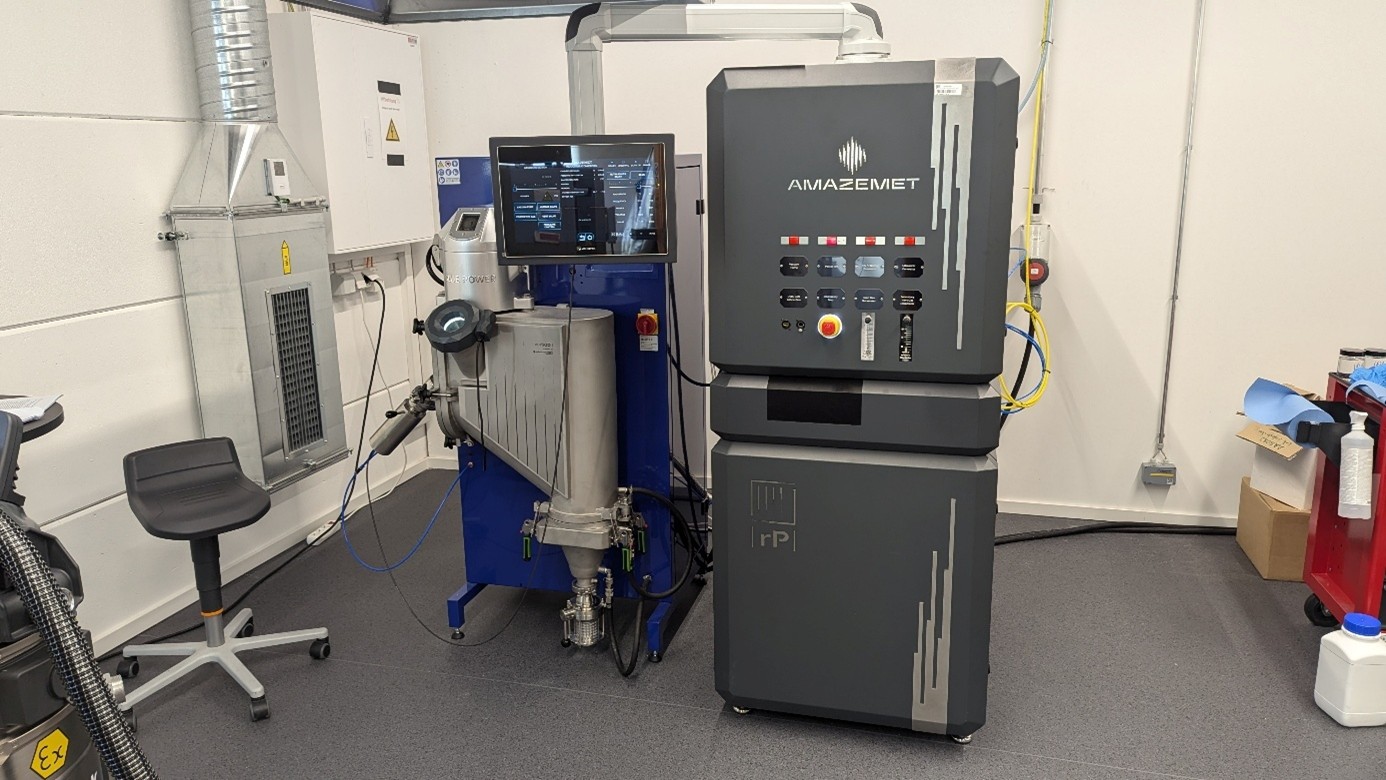
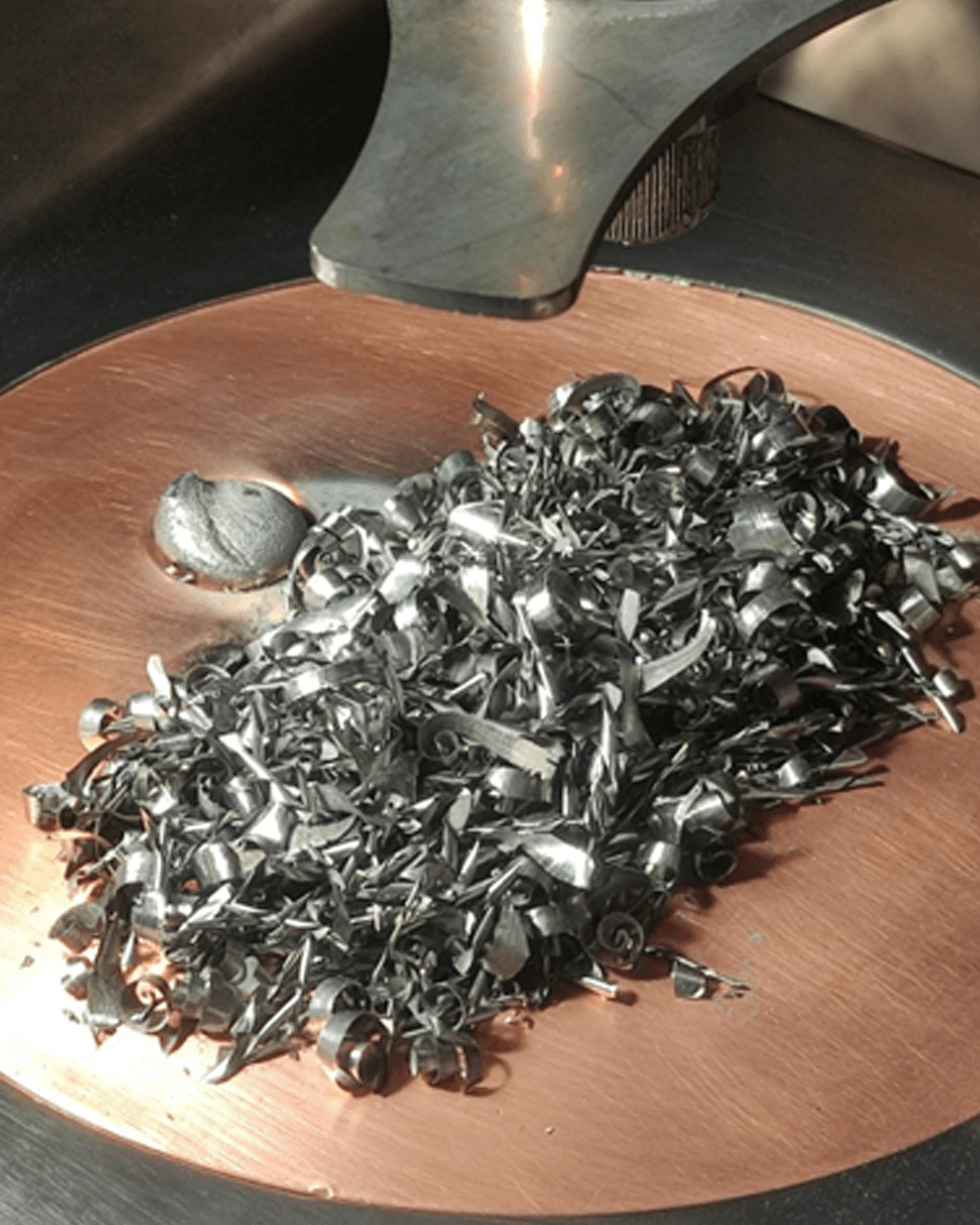
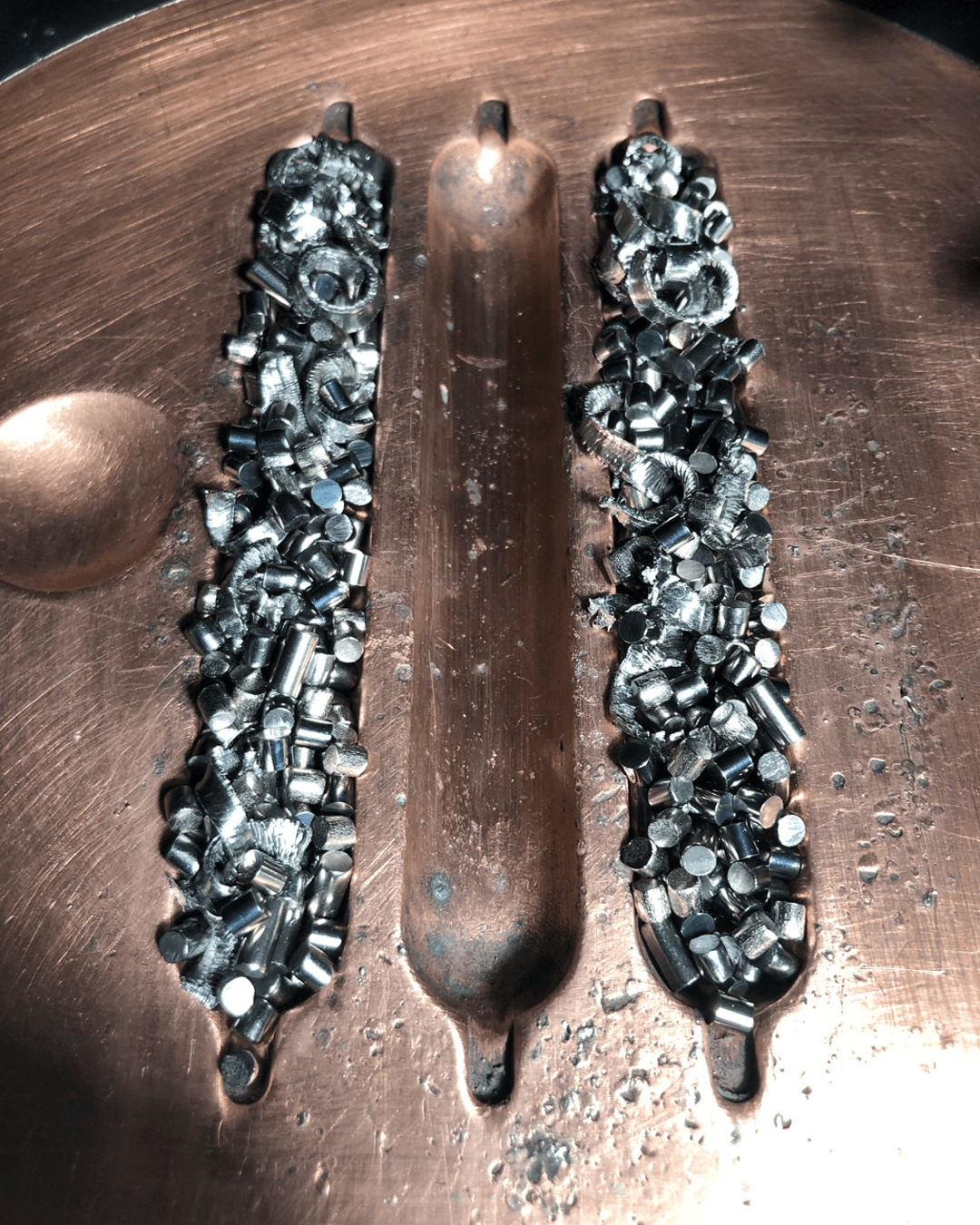
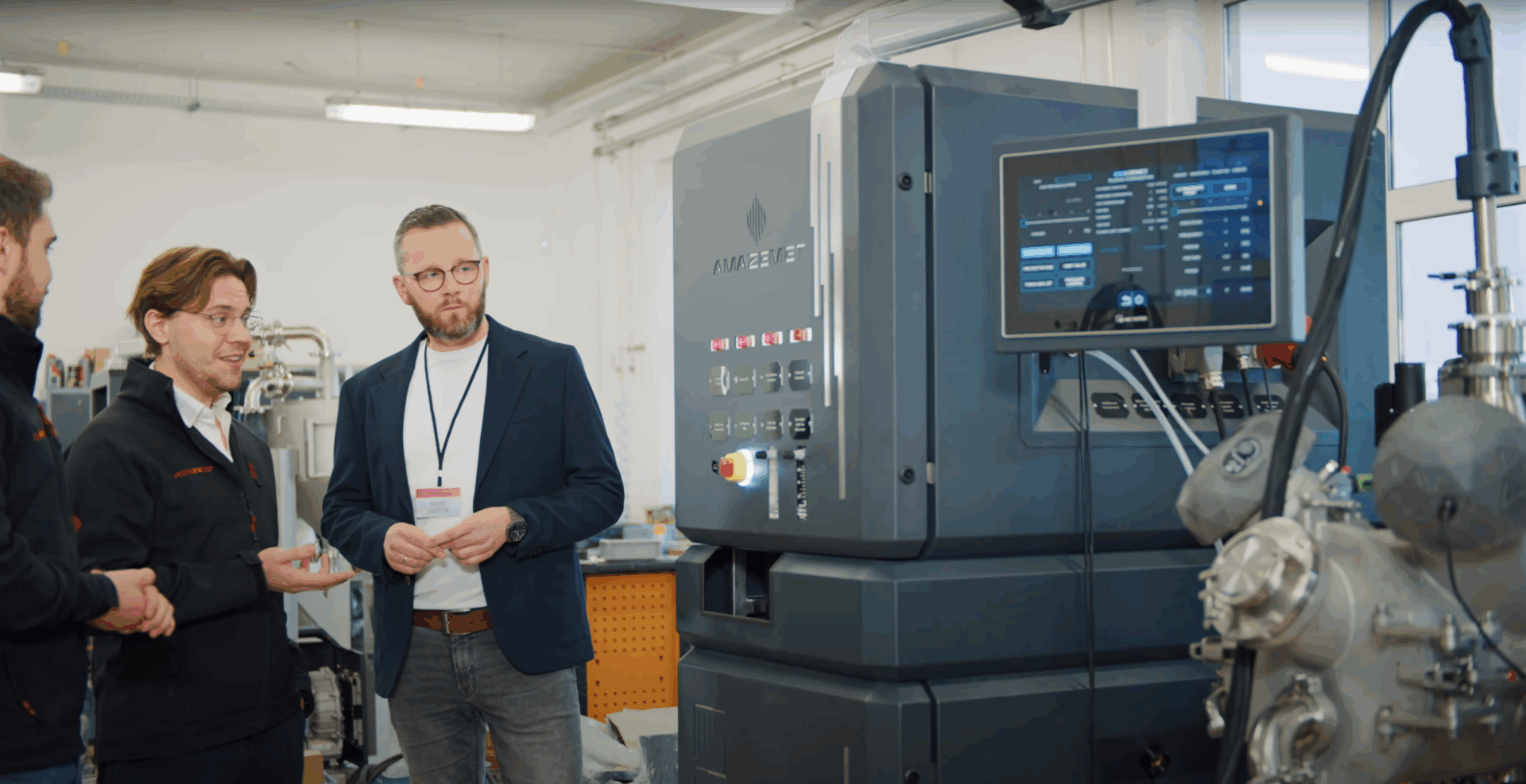
Freedom in Metal AM Develompent & Production
Close the process chain of additive manufacturing cycle
Join industry leaders and explore AMAZEMET’s technologies – from innovative ultrasonic atomization to advanced heat treatment processes. Create unique powders and novel high-performance materials in-house, and transform your manufacturing capabilities.
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Challenges in Additive Manufacturing Industry
Challenges in Additive Manufacturing Industry
The additive manufacturing industry revolutionized how complex, high-performance components are designed and produced, enabling faster prototyping, reduced material waste, and customized solutions across aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and energy sectors. However the industry faces significant challenges, that demand innovative solutions:
The additive manufacturing industry revolutionized how complex, high-performance components are designed and produced, enabling faster prototyping, reduced material waste, and customized solutions across aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and energy sectors. However the industry faces significant challenges, that demand innovative solutions:
Reliance on Spherical Powders
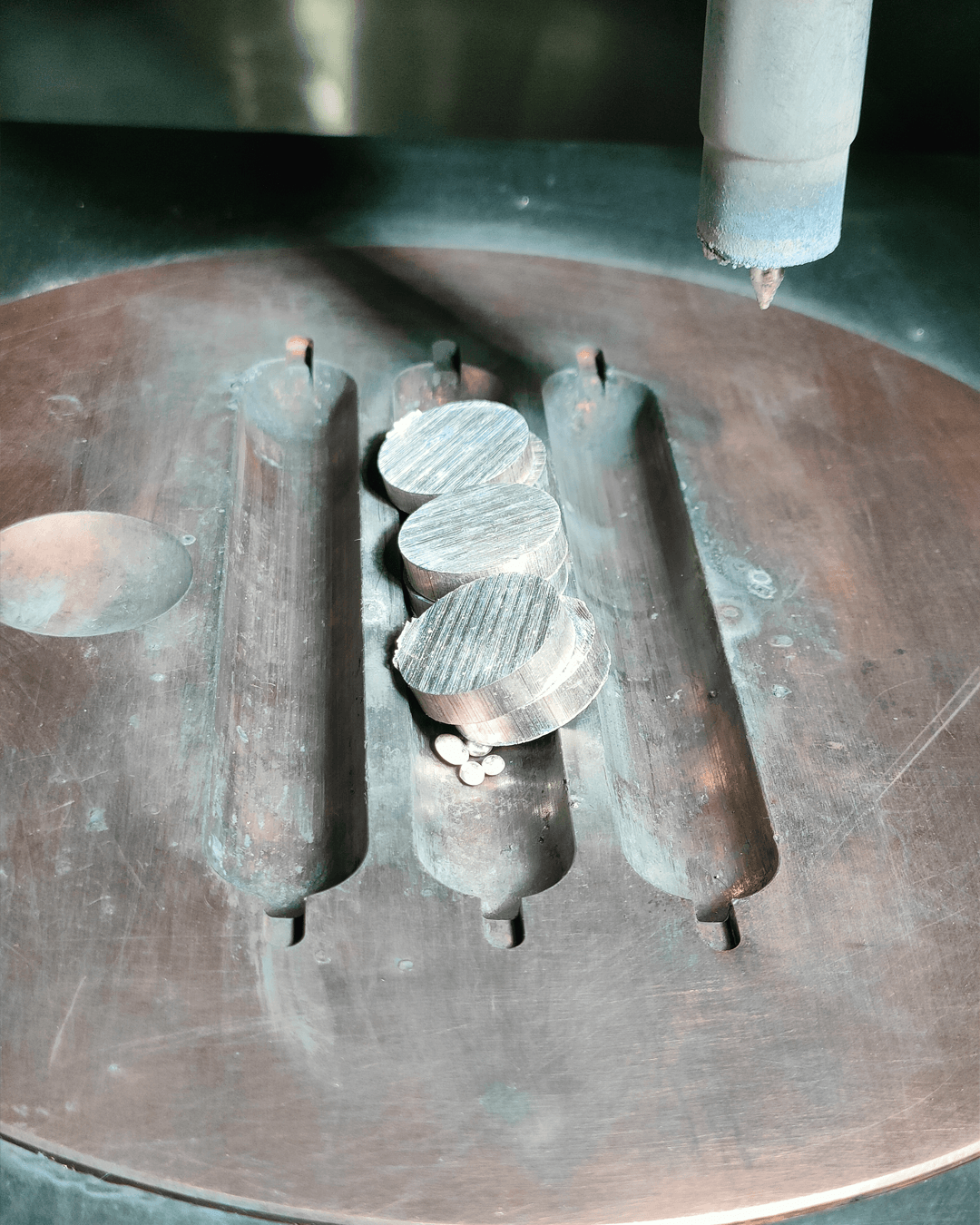
Additive manufacturing relies on spherical powders for optimal flowability and packing density. These powders can be produced using various atomization methods, each suited to specific applications and capable of processing a unique range of materials. Choosing the right atomization method is critical to achieving desired material properties and meeting the stringent requirements of additive manufacturing processes.
Heat Treatment Complexities
Heat treatment of parts obtained via additive manufacturing poses significant challenges due to thermal stresses that can lead to distortion or cracking and the material’s high affinity for oxygen, which increases the risk of surface contamination.
High Costs of Metal Powder Production
Producing high-quality metal powders is often seen as prohibitively expensive. The costs are driven by the energy-intensive nature of traditional atomization methods and the specialized equipment required, which limits accessibility for smaller-scale operations.
Powder Recycling Limitations
Additive manufacturing generates significant amounts of leftover or out-of-spec powders. These powders are often challenging to recycle due to changes in particle morphology, contamination risks, or shifts in chemical composition, leading to increased waste and costs.
Challenges in Advanced Material Development
Developing new materials for additive manufacturing involves overcoming slow, iterative processes that are both time-intensive and costly. This challenge is compounded by the need to tailor materials to specific applications while ensuring they meet stringent performance and quality requirements.

CHOOSE YOUR COMPOSITION
Solutions for Additive Manufacturing Industry
The challenges in the additive manufacturing industry can be addressed through various methods, each offering distinct advantages and drawbacks
01
In the context of powder atomization, different methods impose specific requirements on the feedstock material, which can limit flexibility in developing new powders tailored for 3D printing. For example, gas and plasma atomization require pre-alloyed feedstocks, whereas ultrasonic atomization can process raw elemental materials, providing a more versatile pathway for creating novel powder compositions. However, all methods require careful optimization to produce the high-quality, spherical powders essential for additive manufacturing.
02
When it comes to the heat treatment of titanium and other reactive metals, processes can be conducted in an argon environment to minimize oxidation, followed by mechanical or chemical removal of oxidized layers. Alternatively, heat treatment can involve the use of tantalum wraps or metals with a higher affinity for oxygen, such as steel 316Ti. While these approaches are effective, they often incur high costs and lead to significant losses of strategic raw materials, making them less sustainable for large-scale applications.
03
Achieving a balance between cost, sustainability, and material flexibility is essential for overcoming these challenges and unlocking the full potential of additive manufacturing technologies.
AMAZEMET
3 Myths of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is transforming industries with its potential for innovation and efficiency, but several misconceptions still hinder its wider adoption.
Myth #1
Metal Powder
Production is Expensive
Reality: Ultrasonic atomization technology, provides a cost-effective and efficient alternative for producing high-quality metal powders in-house. It reduces waste and enables tailored powder production, challenging the notion that advanced powders are prohibitively expensive.
Myth #2
Additive Manufacturing
Powders Cannot Be Recycled
Reality: Ultrasonic re-atomization technology, allow for the effective recycling of out-of-spec or leftover powders, that can be reused in additive manufacturing without compromising quality.
Myth #3
Advanced Material Development
is Slow and Costly
Reality: Advancements in technology have revolutionized the development and testing of materials, accelerating innovation by enabling rapid prototyping and experimentation with new alloys. Currently, advanced material development is much more accessible and cost-effective.
AMAZEMET
Pioneering Innovation in Additive Manufacturing
AMAZEMET is a company in the additive manufacturing industry, specializing in advanced material solutions and innovative technologies. As a spin-off from the Warsaw University of Technology, AMAZEMET leverages cutting-edge research and engineering expertise to deliver groundbreaking solutions like rePOWDER, inFURNER, and Powder2Powder, which address the most pressing challenges in alloy development, heat treatment, powder production and recycling. With a focus on sustainability, precision, and efficiency, AMAZEMET has become a trusted partner for industry and academia.
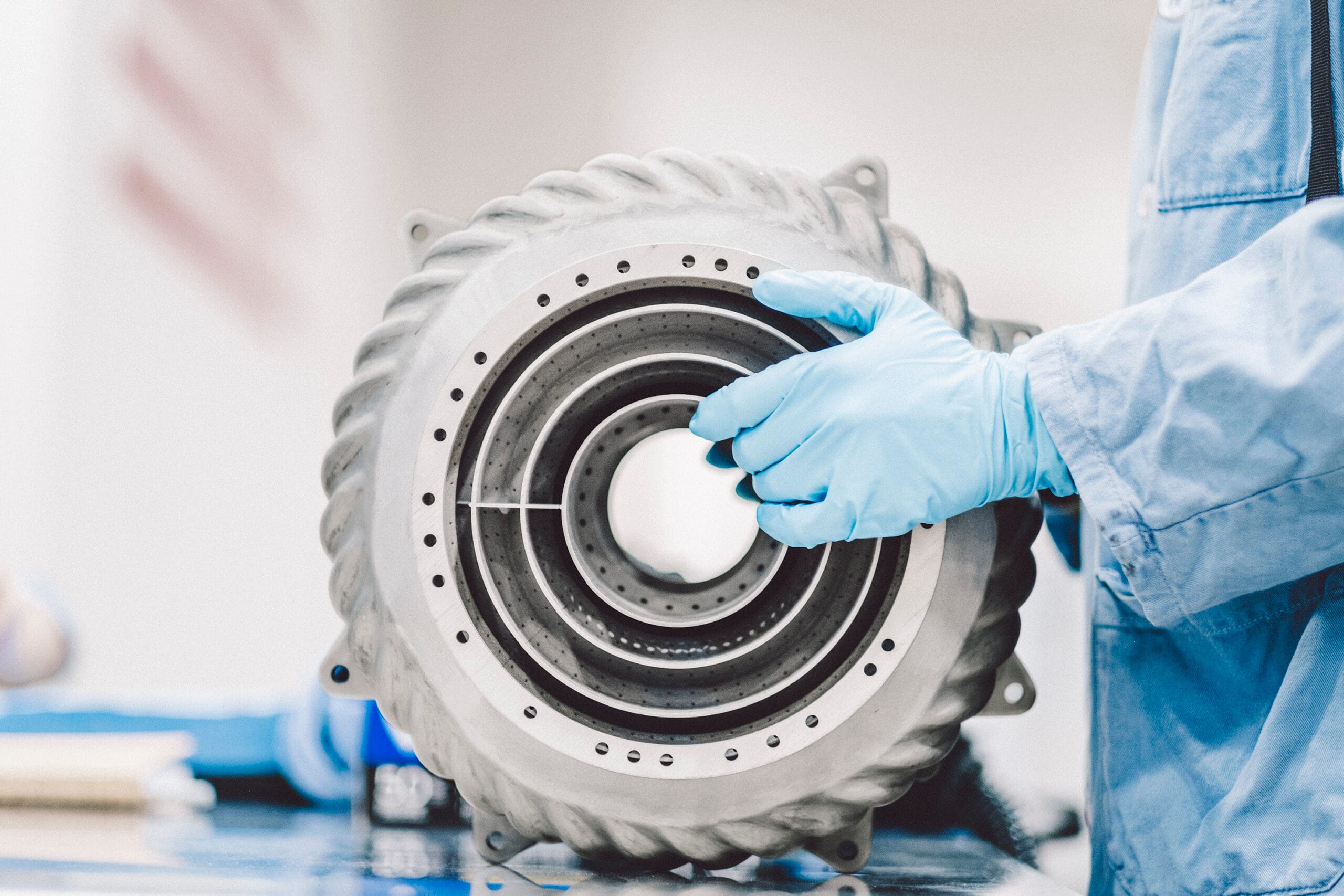

AMAZEMET
Scientific Publications and Industry Collaborations
AMAZEMET actively contributes to the advancement of additive manufacturing and materials science. Explore our recent scientific publications highlighting our innovations:
01
High-Performance High Entropy alloys for heat resistant applications
This paper explores the innovative technology of ultrasonic atomization by employing metal powder-cored wire as a filament to fabricate spherical powders. The method demonstrates a novel approach to generate uniform size distributions of spherical-shaped powders in the range of 30–60 μm, characterized by a homogeneous high-entropy composition. This technique’s significance lies in its ability to efficiently produce High Entropy Alloy (HEA) powder, marking a substantial stride toward energy-efficient routes in material fabrication. The implications extend across multiple industrial sectors, promising new way for advanced materials synthesis and manufacturing processes.
02
Enhancing Additive Manufacturing with Magnetocaloric Ni-Mn-Ga Heusler Alloy-Embedded Polymer Filaments
Magnesium (Mg) and its alloys offer promise for aerospace, railway, and 3D technology applications, yet their inherent limitations, including inadequate strength, pose challenges. Magnesium matrix composites, particularly with metallic reinforcements like titanium (Ti) and its alloys, present a viable solution. Therefore, this study investigates the impact of Ti6Al4V reinforcement on AZ31 magnesium alloy composites produced using pulse plasma sintering (PPS). Results show enhanced microhardness of the materials due to improved densification and microstructural refinement. However, Ti6Al4V addition decreased corrosion resistance, leading to strong microgalvanic corrosion and substrate dissolution. Understanding these effects is crucial for designing Mg-based materials for industries like petrochemicals, where degradation-resistant materials are vital for high-pressure environments. This research provides valuable insights into developing Mg-Ti6Al4V composites with tailored properties for diverse industrial applications, highlighting the importance of considering corrosion behavior in material design. Further investigation is warranted to establish predictive correlations between Ti6Al4V content and corrosion rate for optimizing composite performance.
03
Controlling Crystallization in Metallic Glasses for Part-Specific 3D Printing of In Situ Composites
This research presents a comprehensive study on the production of aluminum-matrix composite (AMC) powders using ultrasonic atomization for additive manufacturing (AM). The impact of different heat sources—plasma, arc, and induction melting—was evaluated on the processability and resultant properties of the AMC powders, including morphology, size, and composite structure. Additionally, induction melting was considered in terms of process parameters such as pressure difference, nozzle size, and frequency. The analysis of AMC powder processability revealed that the efficiency of the ultrasonic process depended on the selected heat source. The highest efficiency, nearly 50%, was attained with the induction system. All produced AMC powders exhibited high sphericity, with average sizes ranging from 88.2 to 120 µm. However, the desired composite structure was not achieved under tested conditions due to the decrease in SiC particle content from 20% in the feed material to approximately 3.5% in the final AMC powder. Based on these results, the research highlights the potential and limitations of ultrasonic atomization in AMC powder production, emphasizing the need for further optimization to improve powder quality and process efficiency for broader industrial application in AM.
WHY AMAZEMET
Solutions for Additive Manufacturing
In the rapidly evolving landscape of additive manufacturing, the ability to innovate and adapt is crucial. AMAZEMET offers advanced solutions that address key challenges in the industry, paving the way for enhanced material development, recycling efficiency, and precision manufacturing.
rePOWDER
Alloy development for additive manufacturing
rePOWDER revolutionizes alloy development for additive manufacturing by enabling the efficient production of tailored metal powders. With ultrasonic atomization technology, users can create high-quality powders in-house, designed to meet specific application requirements, accelerating the development of innovative materials and reducing reliance on external suppliers.
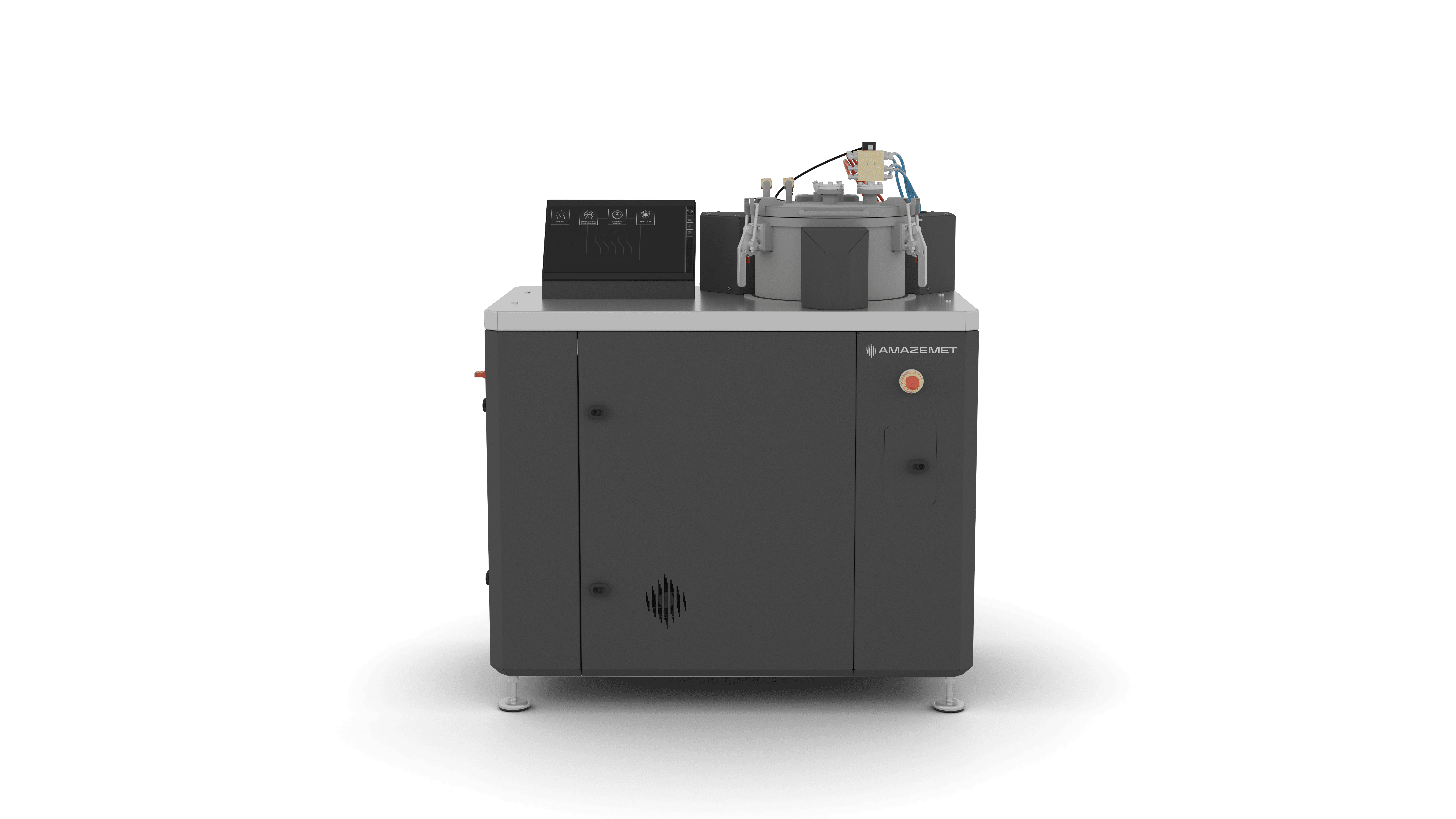
inFURNER
Alloy development for additive manufacturing
rePOWDER revolutionizes alloy development for additive manufacturing by enabling the efficient production of tailored metal powders. With ultrasonic atomization technology, users can create high-quality powders in-house, designed to meet specific application requirements, accelerating the development of innovative materials and reducing reliance on external suppliers.
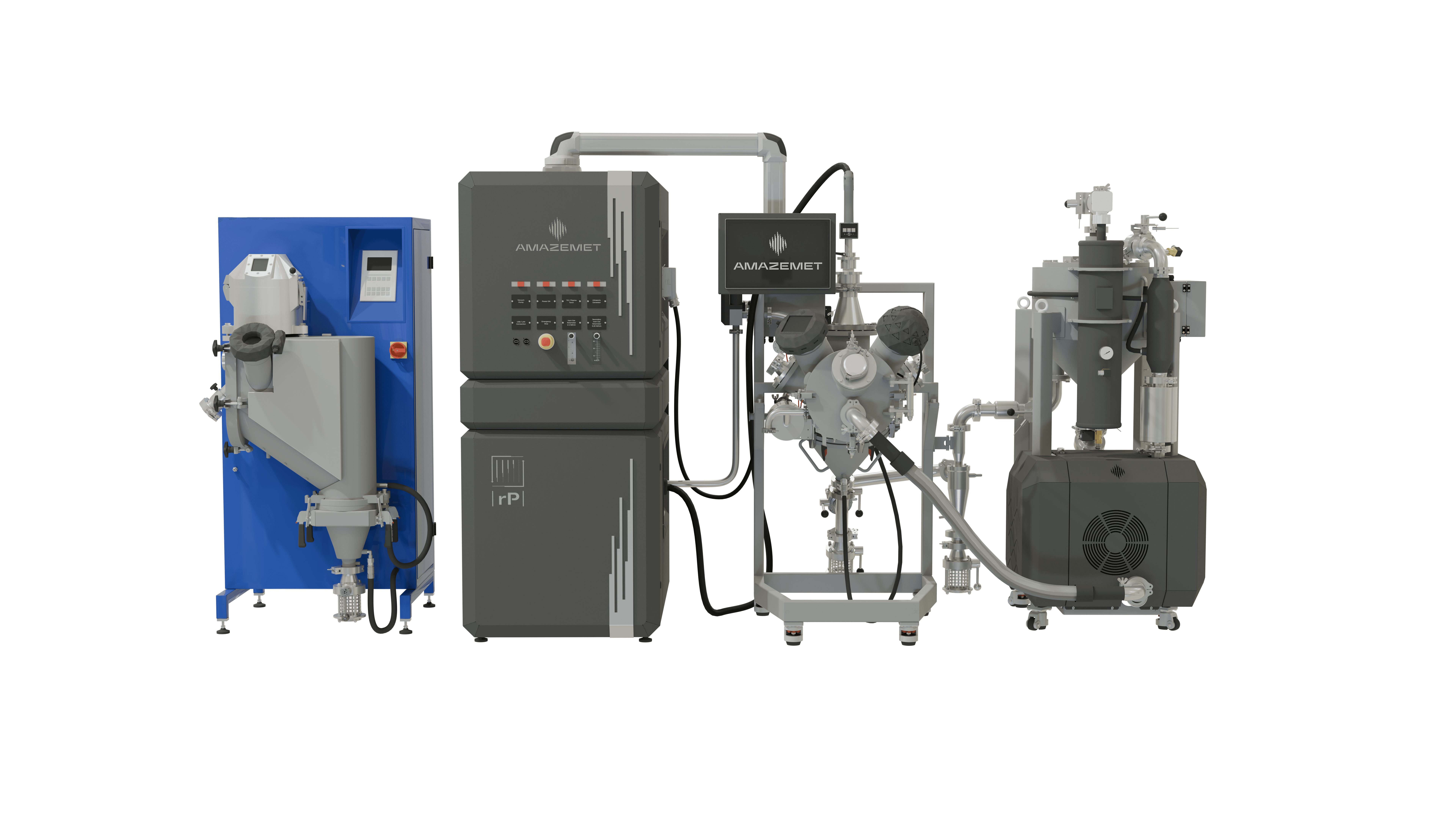
Powder2Powder
Re-atomization of out-of-spec powders and in-situ alloy formation from powder blend
Powder2Powder addresses the growing need for sustainability by reatomizing out-of-spec powders and transforming them into reusable materials. It also enables in-situ alloy formation from powder blends, offering a versatile approach to material recycling and customization, which helps manufacturers reduce waste and expand their material options.
Services
Atomization, welding or any other task
AMAZEMET thanks to their R&D center with independent machine part take part iny many actions with multidisciplinary works needs to be done. Solving the challenges related to ultrasonic atomization enables us to realize various tasks in additive manufacturing sector.
Together, these solutions empower manufacturers to innovate with confidence, streamline processes, and achieve sustainability goals, positioning AMAZEMET as a key player of progress in the additive manufacturing industry.
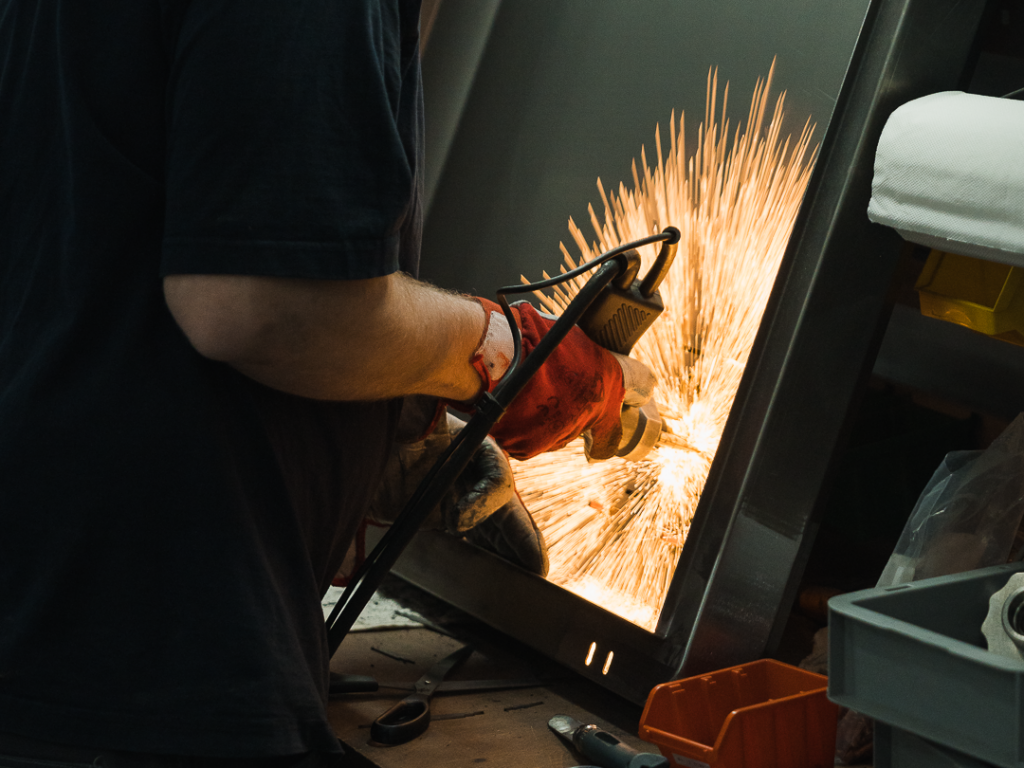
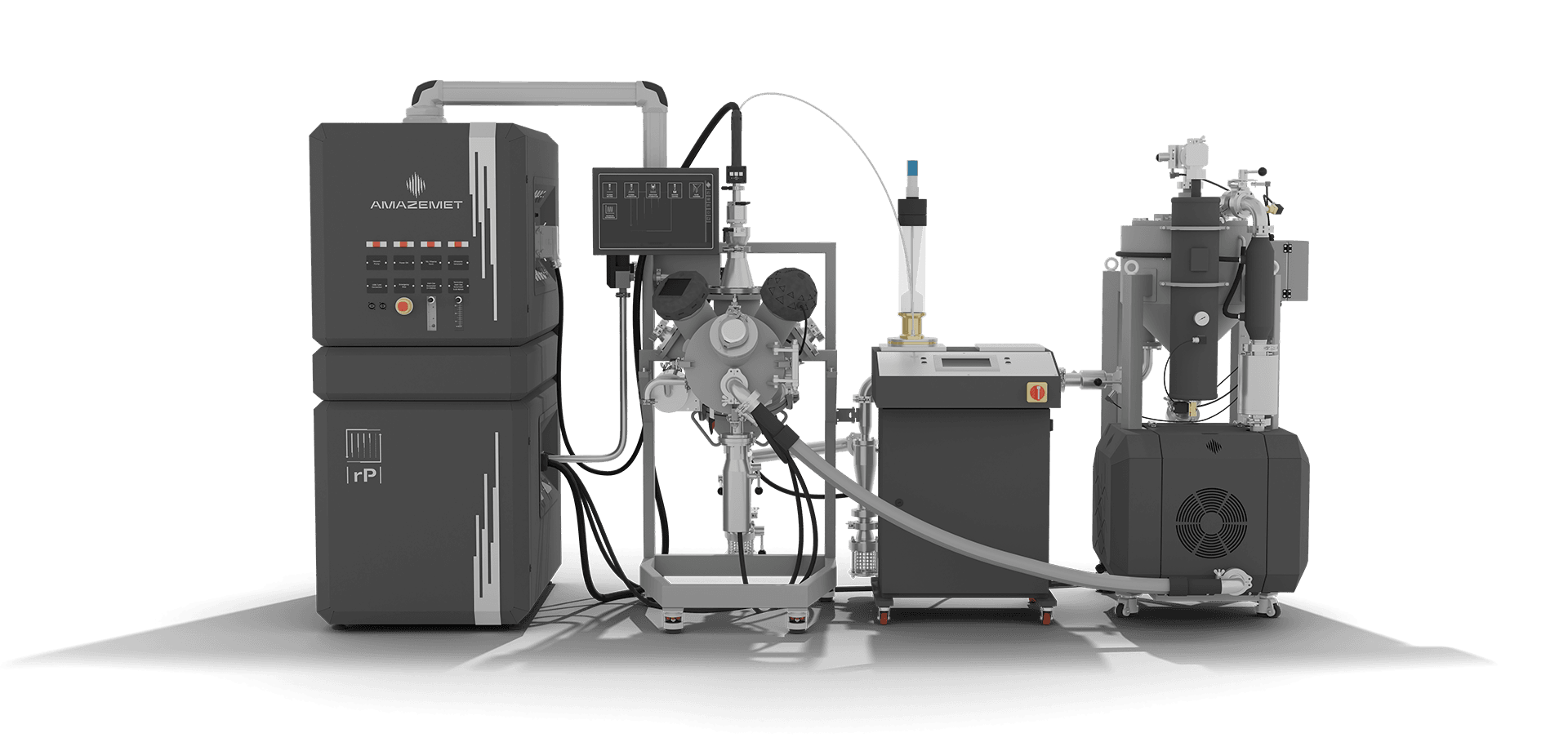

FREEDOM IN METAL AM
DEVELOPMENT & PRODUCTION
RESEARCH PARTNERSHIP
Unlock Collaborative Research
Opportunities in Additive Manufacturing
At AMAZEMET, we specialize in advancing additive manufacturing capabilities through cutting-edge research and technologies. Whether you’re exploring solutions for high-performance alloys, optimizing recycling processes, or tackling material development challenges, we’re ready to collaborate. Discover how our innovative ultrasonic atomization, powder recycling, and heat treatment technologies can accelerate your R&D efforts.
Ready to explore new possibilities in additive manufacturing? Click below to learn more about our R&D opportunities.
ENABLING MATERIALS FOR CUTTING-EDGE APPLICATIONS
Explore Our Work in Action
Discover how AMAZEMET supports research and innovation through real-world collaborations and deep technical insights
Case Studies
Our case studies showcase how we’ve supported partners across industries with tailored solutions—from alloy development to process optimization. They focus on real challenges and how our technology helped turn ideas into results.
Application Notes
Application notes provide a deeper look into the technical aspects of our systems, methods, and materials. They’re ideal for researchers and engineers seeking detailed knowledge and insights to guide their own experiments and development work.
LET’S TALK
Close the loop in your additive manufacturing process and unlock new possibilities
Explore AMAZEMET’s state-of-the-art technologies – from ultrasonic atomization and powder recycling to high-vacuum heat treatment. Transform your manufacturing capabilities, innovate with confidence, and achieve sustainability goals.

Contact us today to get a quote for your customized rePOWDER setup.