
The Role of Additive Manufacturing in Sustainable Metal Production
Additive manufacturing (AM) is revolutionizing the production of metal parts, particularly in terms of sustainability. By leveraging innovative 3D printing techniques, AM allows for the precise and efficient production of metal parts, dramatically reducing waste and energy consumption. As industries strive for greener alternatives, AM is playing a pivotal role in driving sustainability across various sectors, from aerospace to automotive.
In this article, we’ll explore 10 key advantages of additive manufacturing for sustainable metal production, demonstrating how this emerging technology is reshaping the future of metalworking while promoting environmental responsibility.
1. Reduction in Material Waste
One of the most significant advantages of additive manufacturing is the reduction in material waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on subtractive processes, such as machining or casting, which can generate substantial amounts of scrap material. In contrast, additive manufacturing builds parts layer by layer, using only the material necessary for the component. This efficient use of raw materials is a fundamental step toward minimizing waste in metal production.
AM has the potential to reduce waste by up to 90%, offering a much-needed solution for industries aiming to lower their environmental footprint.
2. Energy Efficiency in Metal Production
While traditional metalworking processes can be energy-intensive, additive manufacturing provides a more energy-efficient alternative. The layer-by-layer nature of the process means that less energy is required compared to techniques like forging or casting, where large amounts of heat are necessary to shape metal parts.
AM processes often operate at lower temperatures, making them more energy-efficient and reducing the overall carbon footprint of production.
3. Customization and Design Flexibility
Another advantages of additive manufacturing are the unprecedented design flexibilities it offers. Traditional manufacturing methods are limited by the need for molds, tooling, and machining constraints. However, with 3D metal printing, designers can create complex geometries and optimize structures without the need for costly retooling.
This design freedom opens up new possibilities for creating parts with unique features, such as lattice structures, internal channels, and lightweight components, that would be difficult or impossible to produce with conventional methods.
4. Lower Carbon Footprint
Additive manufacturing contributes to a lower carbon footprint in metal production by reducing the need for transportation and waste disposal. Since the process is highly localized, manufacturers can produce parts closer to the point of use, minimizing the carbon emissions associated with shipping materials over long distances.
Additionally, additive manufacturing reduces the need for extensive machining, which further cuts down on the energy required to shape metal components.
5. Faster Prototyping and Production
One of the key advantages of additive manufacturing is its ability to speed up both prototyping and production. With traditional methods, creating prototypes can be time-consuming and costly. In contrast, AM allows for rapid prototyping, enabling engineers to test designs quickly and iterate on their ideas faster.
This speed is especially beneficial for industries that require short lead times, as it allows companies to bring products to market more quickly, saving both time and resources.
6. Less Scrap Material
Traditional manufacturing processes generate a significant amount of scrap material, which either goes to waste or requires recycling. With additive manufacturing, however, the process is more material-efficient, meaning less scrap is produced. In fact, many AM technologies can reuse metal powder, further reducing waste.
This closed-loop process, where metal powders can be recycled and reused, supports a more sustainable production cycle.
7. On-Demand Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing allows for on-demand production, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing storage costs. This means manufacturers can produce parts only when they are needed, reducing waste associated with overproduction.
With on-demand manufacturing, companies can streamline their supply chains, produce parts closer to their final destination, and reduce waste throughout the production process.
8. Advanced Materials Utilization
Additive manufacturing enables the use of advanced metal materials that may be difficult to machine or shape using traditional methods. This includes high-performance alloys, composites, and metals with complex compositions. As industries demand more specialized materials for their applications, AM technologies are rising to the challenge, offering the versatility to process these advanced materials with high precision.
In the context of AM, metal powders are a key component, and the ability to work with a variety of these advanced materials makes the technology increasingly valuable across various sectors.
9. Tool-Free Manufacturing
One of the standout advantages of additive manufacturing is that it is tool-free. Unlike traditional methods that rely on molds, dies, and other tooling equipment, AM builds parts directly from a digital file. This removes the need for costly and resource-intensive tools, saving manufacturers both time and money.
Tool-free production also allows for customization on a much larger scale, as each part can be unique without incurring additional setup costs.
10. Support for Circular Economy
The concept of a circular economy is becoming increasingly important in the pursuit of sustainability. Additive manufacturing plays a role in this by enabling the reuse and recycling of materials. Metal powders used in AM processes can often be recycled, reducing the demand for raw materials and supporting a circular economy.
By using recycled powders and materials, manufacturers can close the loop on their production processes, further contributing to environmental sustainability.
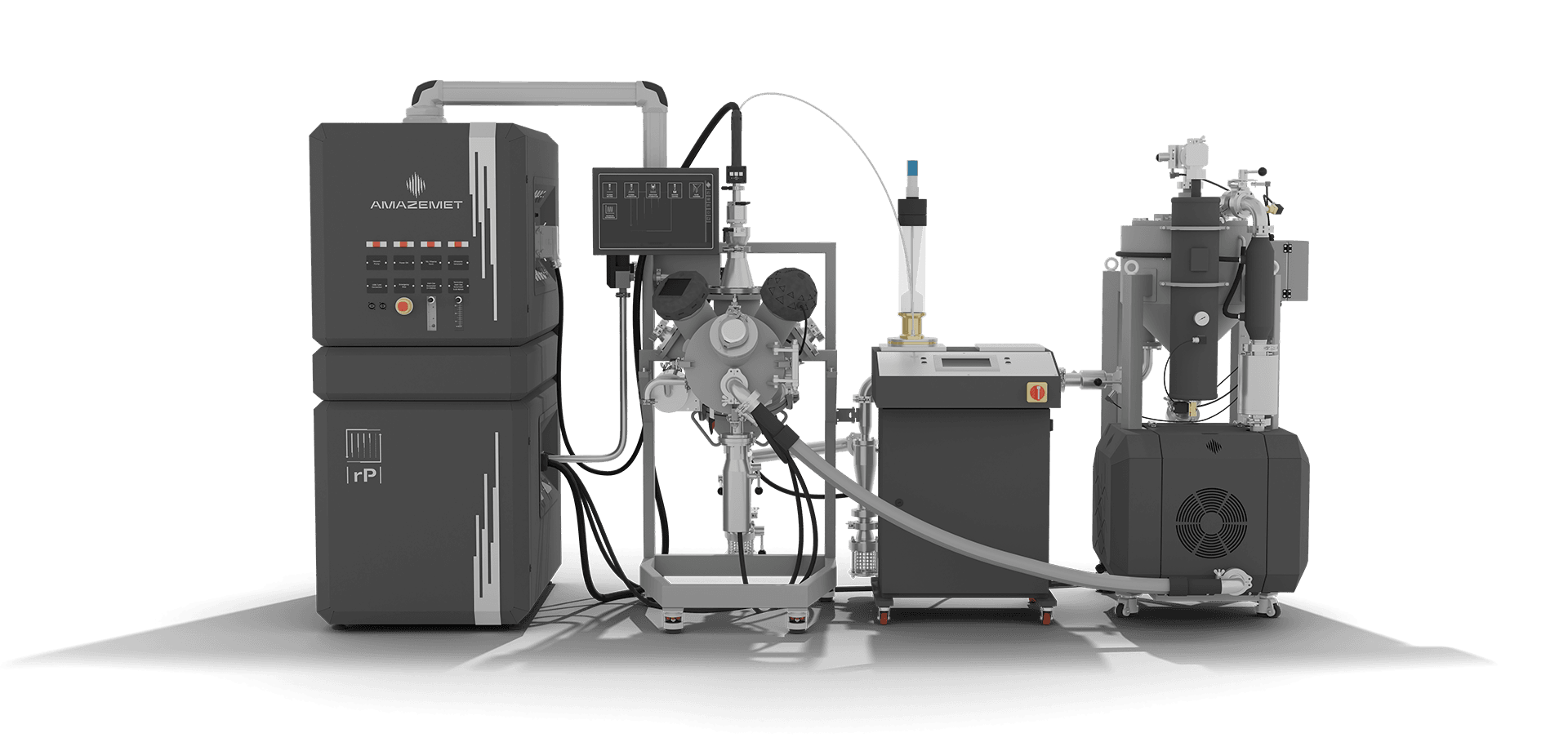
How AMAZEMET Supports Sustainable Additive Manufacturing
At AMAZEMET, we are committed to supporting sustainable metal production through our ultrasonic atomization technology. Our process ensures that high-quality metal powders are produced with minimal waste and energy consumption, making it a perfect fit for industries leveraging additive manufacturing for sustainable metal production.
With our Powder2Powder module, it is possible to directly reatomize powders that are out of spec, irregular or have been used in previous production runs and requires refurbishment, reducing the need for new raw materials and closing the loop on powder usage.
Whether you’re looking for high-performance metal powders for additive manufacturing or need a custom solution for your project, AMAZEMET is here to help.
For more information about our products and services, visit our Metal Additive Manufacturing page.





