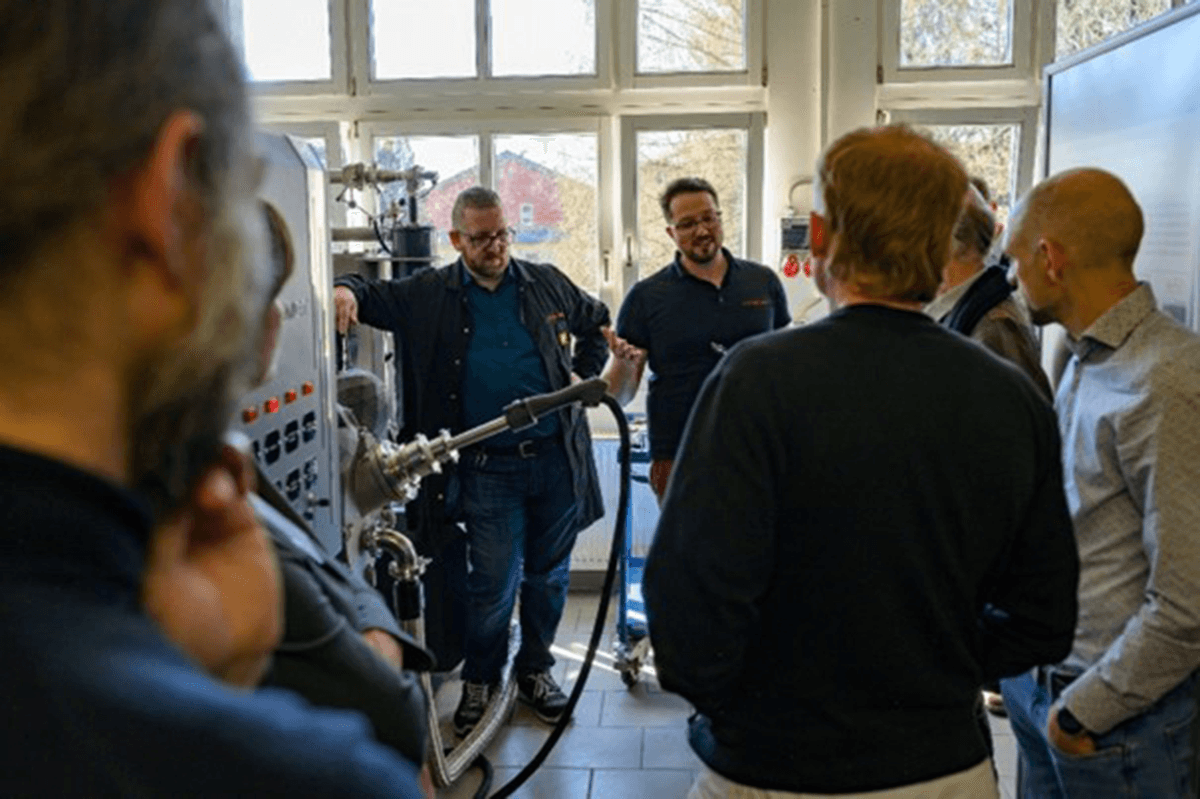
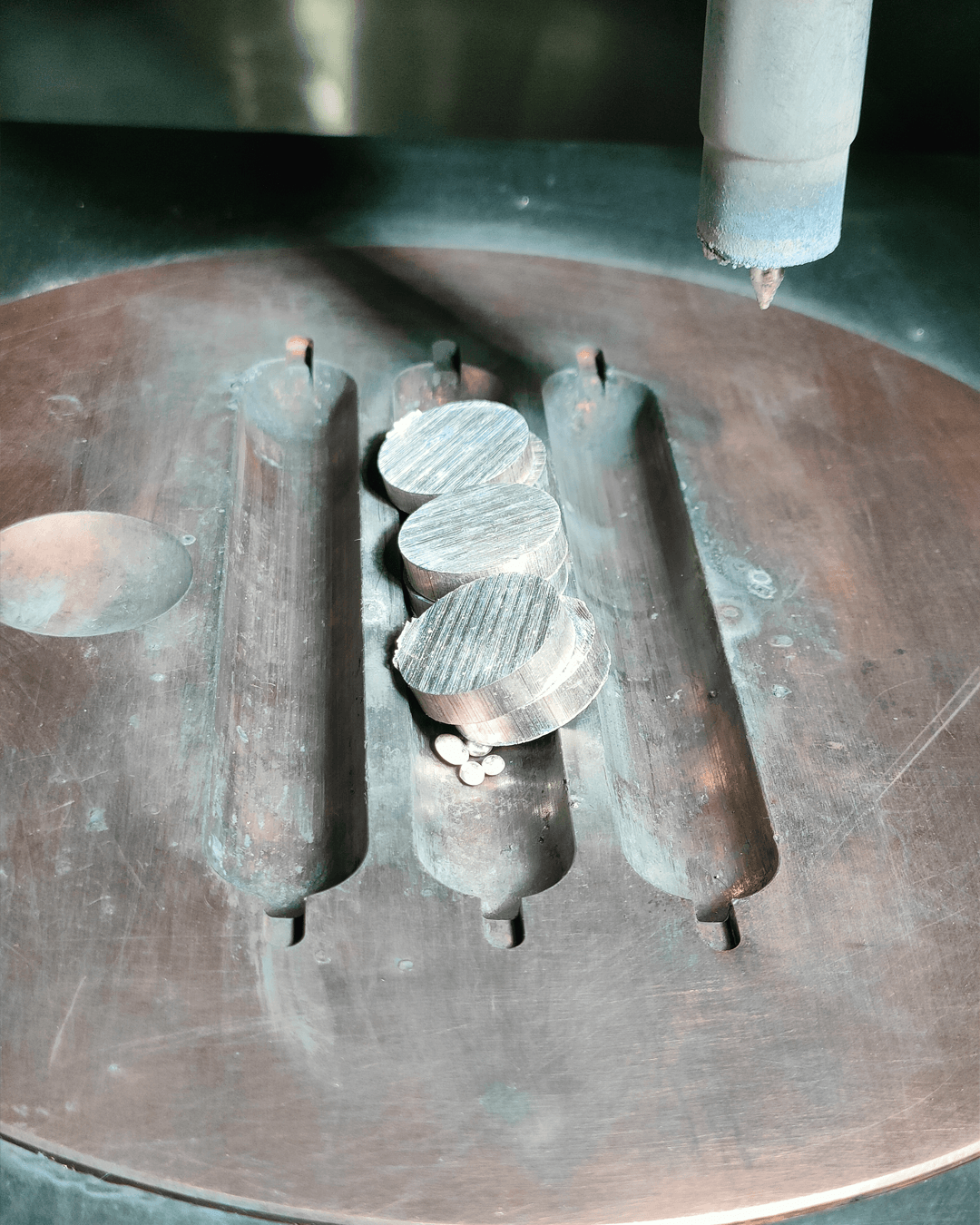
Freedom in Metal AM Develompent & Production
Medical Industry: Advancing Biomedical Materials for Healthcare
The rapid advancements in biomedical engineering rely on cutting-edge material science to improve patient care and surgical outcomes. The development of innovative biomaterials, such as titanium alloys, nitinol, and biodegradable metals, like magnesium and zinc alloys is revolutionizing the medical field. By leveraging advanced manufacturing processes, researchers and healthcare providers can enhance implant longevity, optimize biocompatibility, and develop patient-specific solutions for a wide range of medical applications.
INTRODUCTION
Innovative Material Solutions for Advancing Medical Engineering
The medical industry relies on innovative material solutions to develop biocompatible implants, surgical tools, and patient-specific devices. High-performance materials such as titanium, nitinol, and magnesium play a critical role in modern healthcare, requiring precise processing techniques for enhanced performance and safety. Ultrasonic atomization, high-vacuum heat treatment, and sustainable powder recycling are key to driving progress in biomedical engineering.
MEDICAL INDUSTRY
Challenges in Biomedical Industry
Challenges in Biomedical Industry
The biomedical materials sector faces several key challenges in optimizing materials for implants and medical devices. From controlling the Ni:Ti ratio in nitinol for shape memory effects to overcoming the difficulties in recycling magnesium for biodegradable implants, precision in material processing is critical to enhancing performance, safety, and long-term patient outcomes.
The biomedical materials sector faces several key challenges in optimizing materials for implants and medical devices. From controlling the Ni:Ti ratio in nitinol for shape memory effects to overcoming the difficulties in recycling magnesium for biodegradable implants, precision in material processing is critical to enhancing performance, safety, and long-term patient outcomes.
Nitinol – influence of the Ni:Ti ratio on the shape memory effect
Nitinol, a shape memory alloy widely used in vascular stents, demands highly controlled processing for optimal mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. As a reactive material, nitinol requires precise handling to prevent contamination during atomization and processing. Additionally, the ratio of nickel (Ni) to titanium (Ti) is crucial for determining the critical transformation temperatures, directly affecting its superelastic and shape-memory behavior.
Recycling Magnesium for Biodegradable Implants
Magnesium-based materials offer promising applications for resorbable implants, reducing the need for secondary surgeries. However, efficient recycling and re-atomization of magnesium powders remain a technological barrier due to their high reactivity.
Heat Treatment of Titanium Implants
Medical-grade titanium alloys require precise heat treatment to optimize their mechanical properties, fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility, ensuring long-term success in orthopedic and dental implants. Due to the high affinity to oxygen heat treatment under inert gas atmosphere forms alpha case on it surface which is why vacuum atmosphere is recommended.
Development of Low-Modulus Titanium Alloys (TNTZ)
Traditional titanium alloys can have high stiffness, leading to stress shielding in implants. New low-modulus titanium alloys, such as Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr (TNTZ), offer enhanced bone compatibility while maintaining high mechanical strength.
Alternative Biomedical Materials
- Tantalum: Highly corrosion-resistant and biocompatible, tantalum is ideal for orthopedic implants and bone scaffolds, promoting osseointegration.
- Cobalt-Chromium Alloys: Widely used in joint replacements, these alloys offer excellent wear resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-load applications.

CHOOSE YOUR COMPOSITION
Current market possibilities
The biomedical materials market is evolving with new technologies and methods aimed at improving the production, recycling, and optimization of medical alloys. From atomization processes tailored for biomedical powders to sustainable recycling and heat treatment solutions, these advancements are driving innovation in the development of safer, more effective implants and medical devices.
01
Atomization for Biomedical Powders
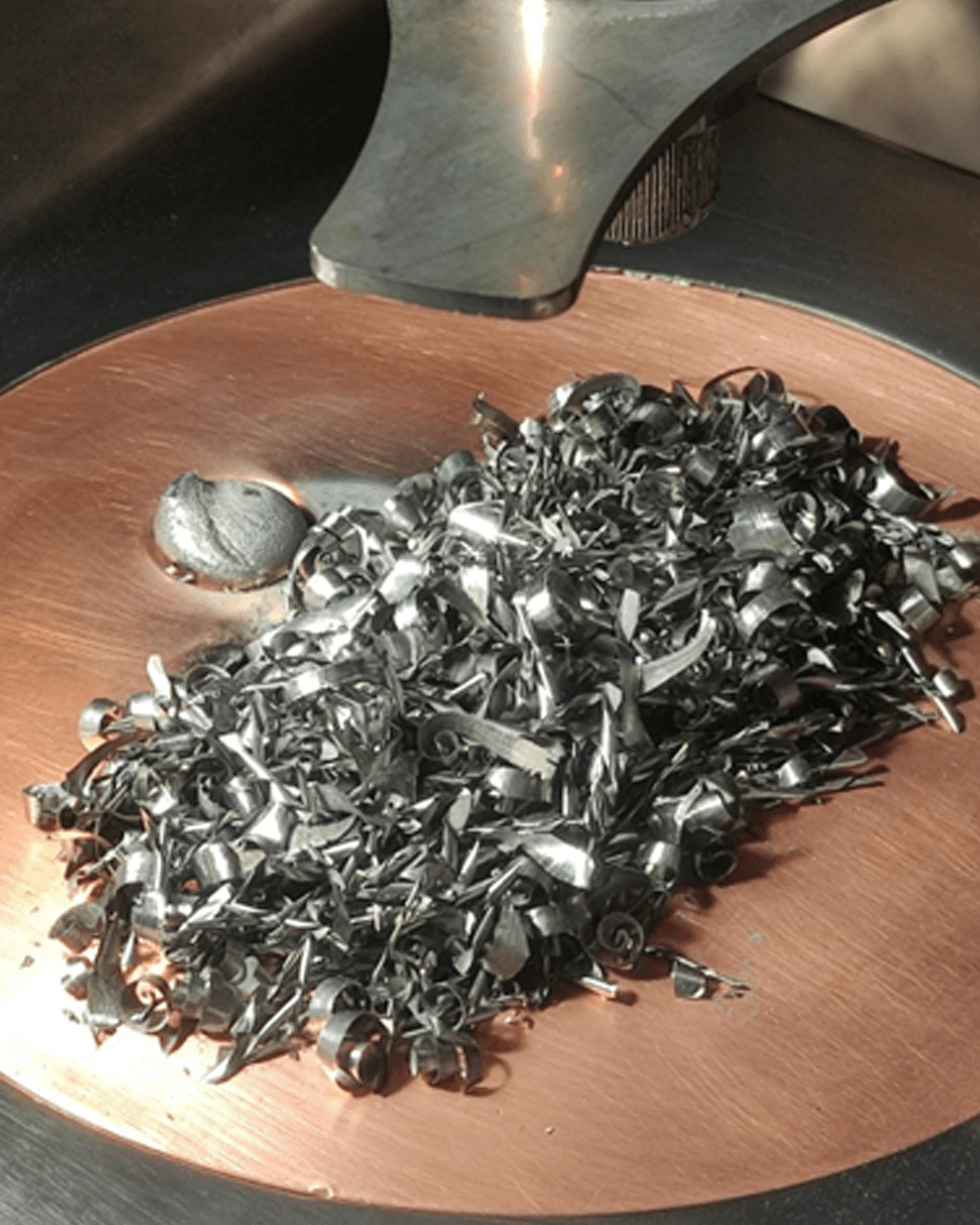
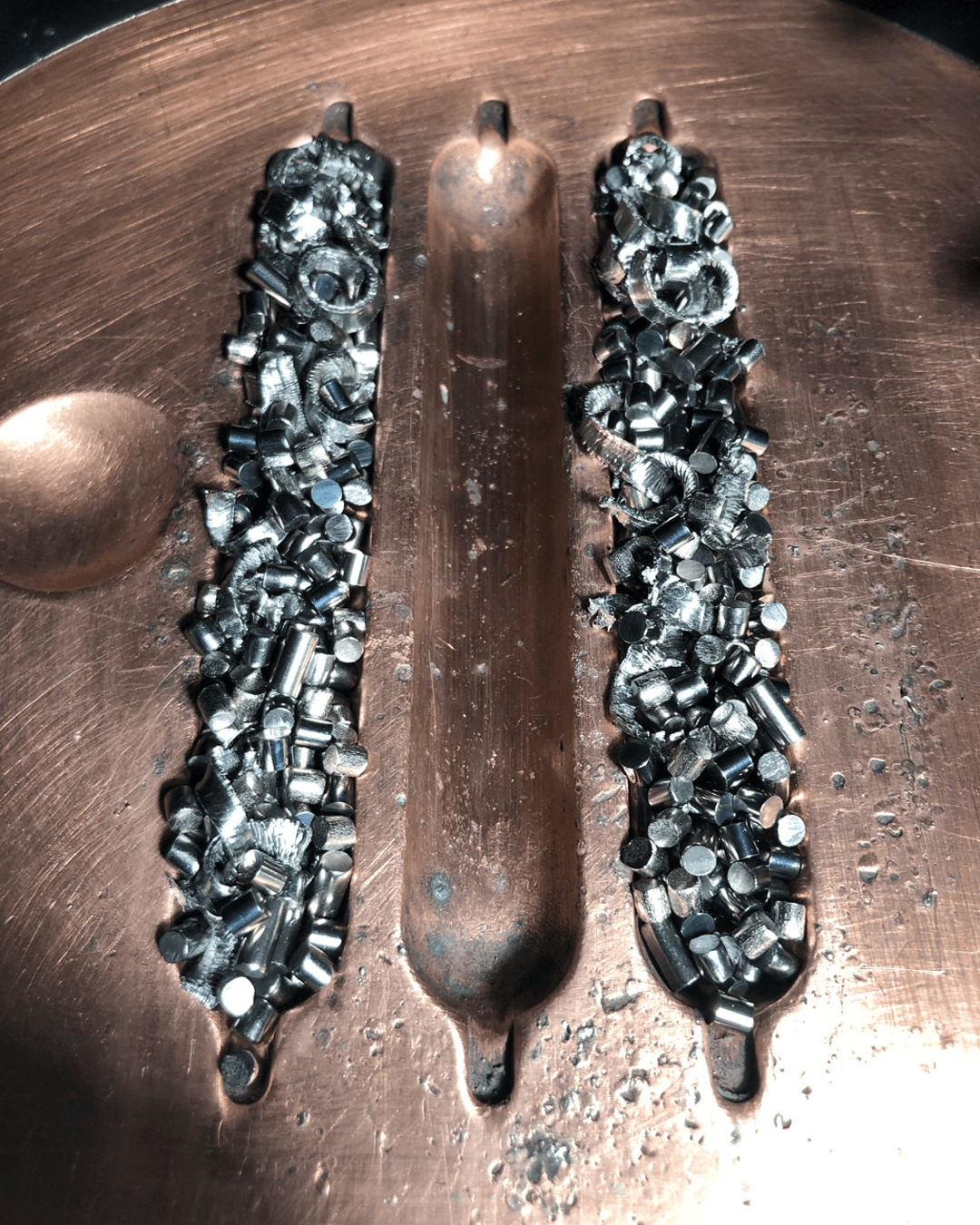
Nitinol, titanium, and magnesium powders can be produced using gas/plasma atomization and EIGA process. However in this methods material can react with the ceramic crucible, requires specific feedstock type (wire or rod), which often for medical grade materials stand in need for production on demand. Additionally, this type of atomization produce wide particle size distribution and forms submicron particles which can increase the risk of powder ignition due to the high reactivity of titanium and magnesium.
02
Sustainable Recycling for Powders
Advanced re-atomization processes enable the recovery and reuse of biodegradable materials, supporting sustainable manufacturing in the medical field.
03
High-Vacuum Heat Treatment for Implan Optimization
Controlled heat treatment processes enhance the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of medical alloys, ensuring safety and durability in implants.
04
Tailored Alloy Development for Medical Applications
Research-driven material innovation, including TNTZ and other biocompatible alloys, helps reduce stress shielding and improve long-term patient outcomes. However the development of materials in powder form is still challenging.
AMAZEMET
Progressing Medical Materials Innovation
As a leader in advanced material processing, AMAZEMET provides cutting-edge solutions for biomedical research and healthcare applications. Our expertise in ultrasonic atomization, high-vacuum heat treatment, and sustainable powder recycling supports the medical industry’s need for high-performance materials in precision medicine.

AMAZEMET
Scientific Publications and EU Projects
AMAZEMET actively contributes to the advancement of biomedical materials through participation in research artiles, European-level research initiatives and collaborative projects. Our involvement in EU-funded programs helps drive innovation in biomaterials, improving their performance and sustainability for medical applications.
01
Comparing the Corrosion Behavior of Dual-Structured Mg-Li Alloys: Laser Powder Bed Fusion vs. Pulse Plasma Sintering
This study explores the use of powder metallurgy methods to fabricate Mg-7.5Li-3Al-Zn alloys from repowdered extruded alloys using ultrasonic atomization. By employing laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and pulse plasma sintering (PPS), the study compares the microstructure and corrosion resistance of the fabricated alloys to their conventionally extruded counterparts, revealing both the advantages and challenges of these advanced manufacturing techniques.
02
Corrosion and Microstructure of Mg-Based Composites from AZ31 and Ti6Al4V via Pulse Plasma Sintering
This research investigates the effect of Ti6Al4V reinforcement on AZ31 magnesium alloy composites produced using pulse plasma sintering (PPS), focusing on their enhanced microhardness and the resulting trade-off in corrosion resistance. The study provides valuable insights for designing corrosion-resistant materials for industries like petrochemicals, where durability under high-pressure conditions is essential.
03
Smart 4D biodegradable metallic shape-shifting implants for dynamic tissue restoration
The EIC-funded BIOMET4D project aims to revolutionize implant design by introducing shape-morphing materials that change over time in response to specific cues, such as magnetic fields. These innovative metallic biodegradable implants hold great potential for dynamic tissue restoration in reconstructive surgeries, offering new solutions for tissue regeneration in applications like ear and nose reconstruction.
WHY AMAZEMET
Solution for medical applications
At AMAZEMET we provide key solutions for medical material development:
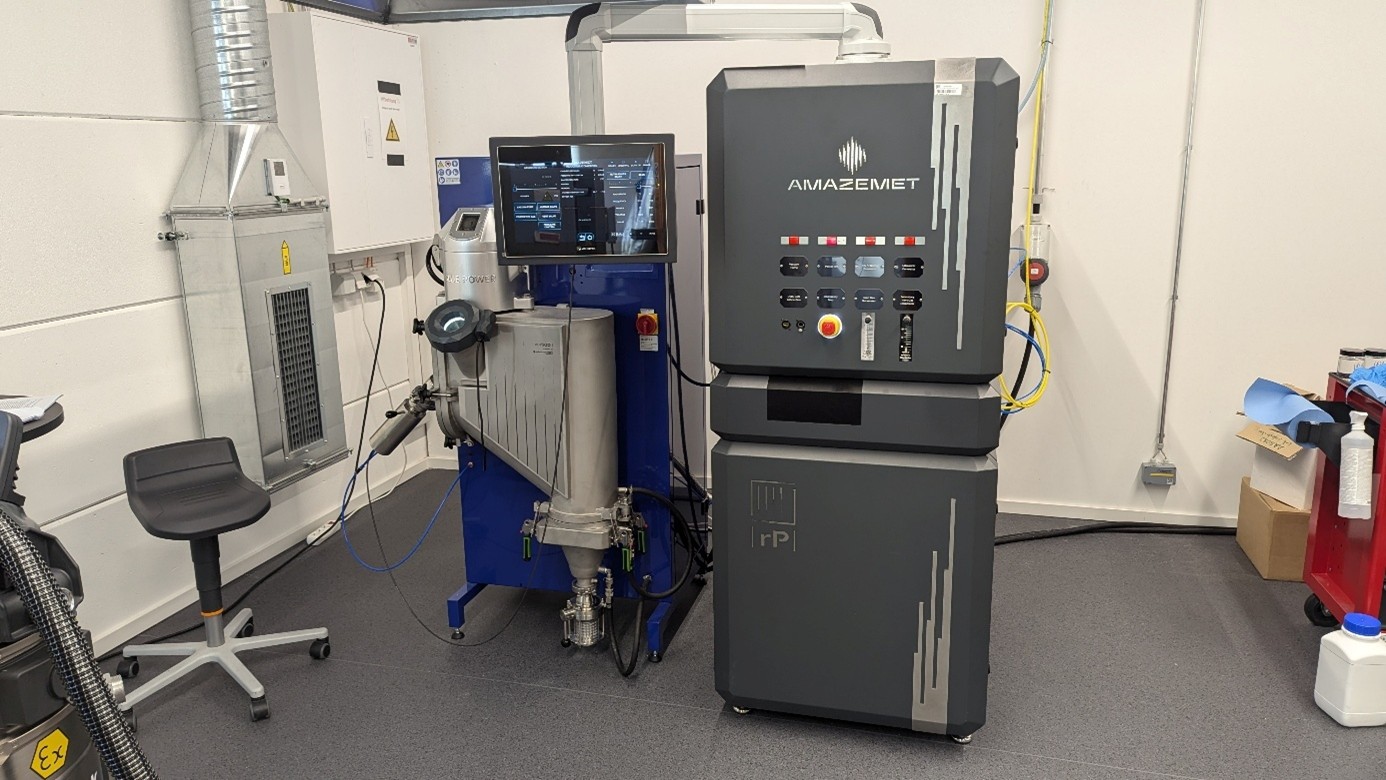
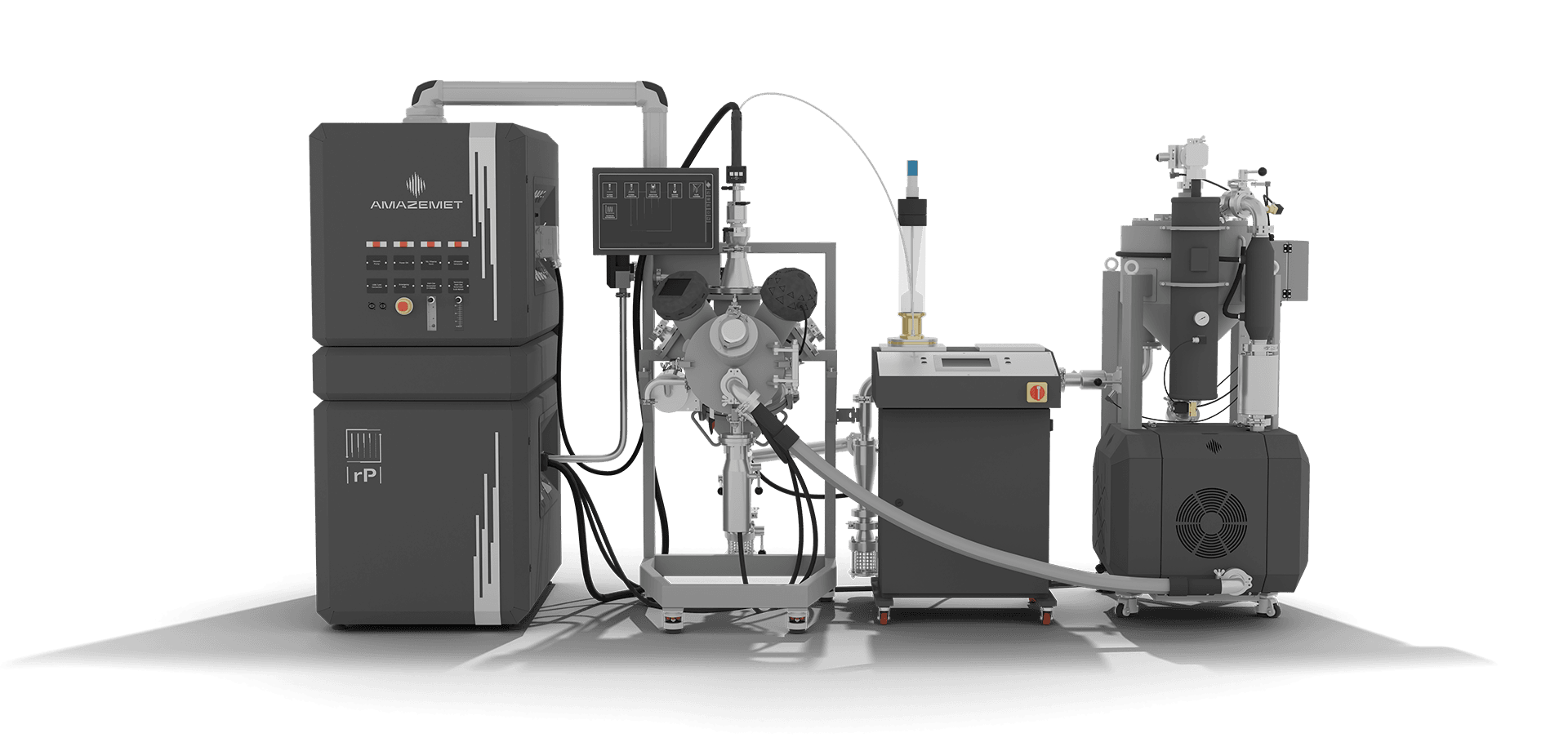
rePOWDER
An ultrasonic atomization system for producing high-purity powders from nitinol, titanium, and magnesium, ensuring superior quality for biomedical applications.
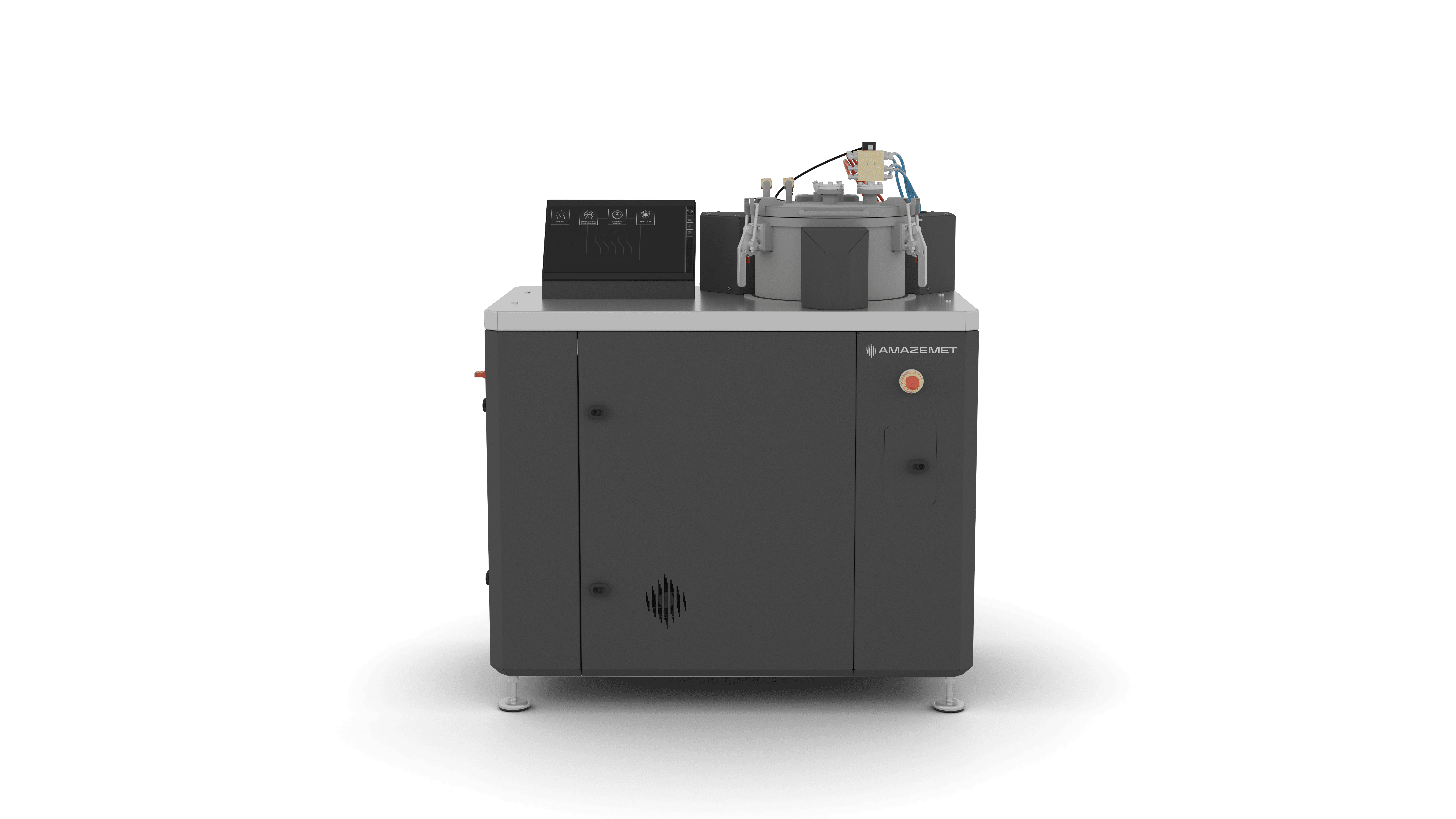
inFURNER
A high-vacuum furnace designed for heat treatment of medical implants, improving their mechanical performance and biocompatibility.
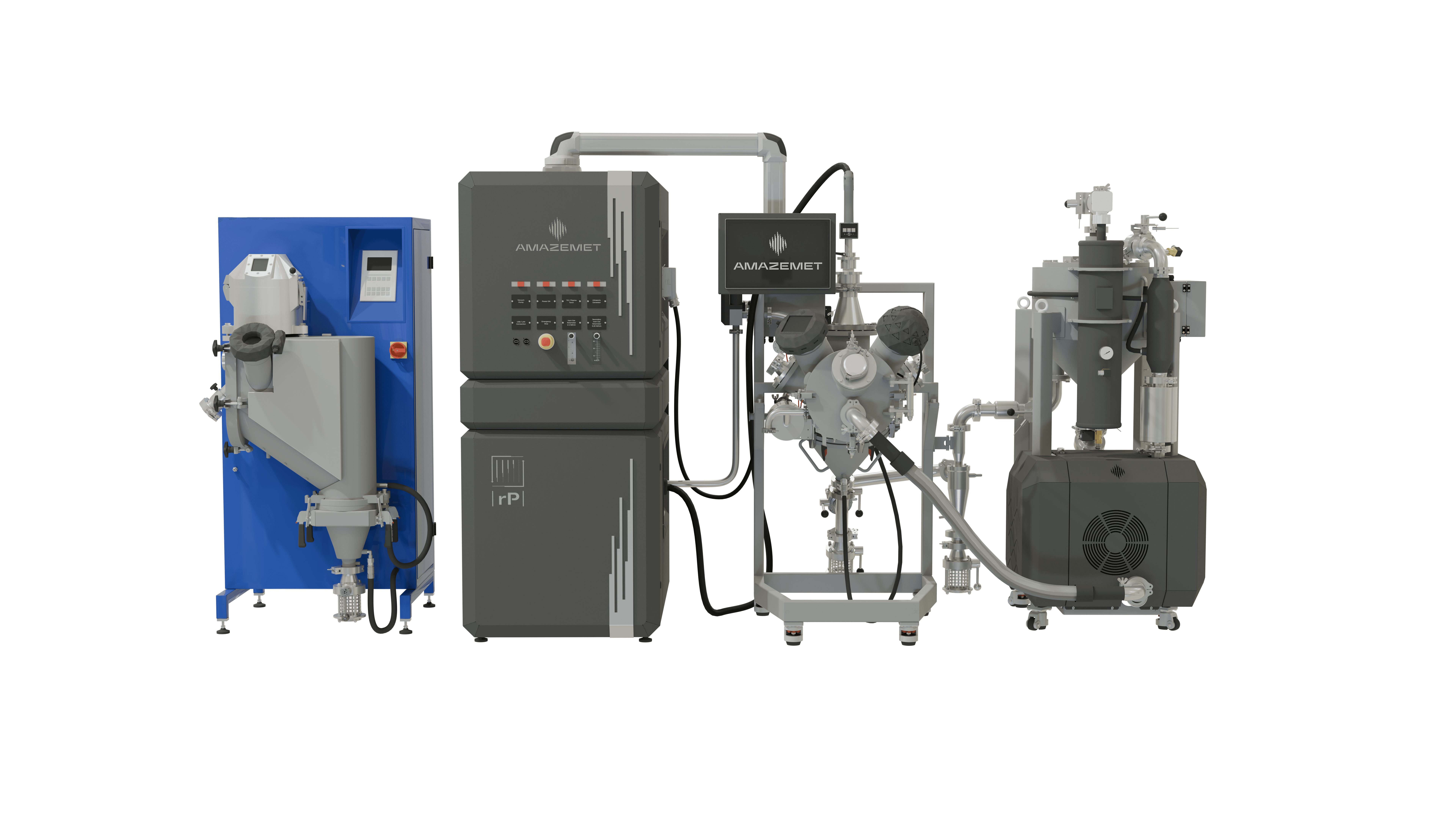
Powder2Powder
A sustainable re-atomization technology that enables the recycling of medical-grade powders, reducing material waste and ensuring consistent quality.
FREEDOM IN METAL AM
DEVELOPMENT & PRODUCTION
RESEARCH PARTNERSHIP
Innovating Biomedical Materials with AMAZEMET: Partnership Opportunities in Medical R&D
Explore groundbreaking opportunities for collaboration in the medical industry with AMAZEMET. Our expertise in advanced material processing, from ultrasonic atomization to high-vacuum heat treatment, empowers the development of high-performance biomedical materials. Partner with us to drive innovation in medical implants, biodegradable alloys, and cutting-edge research that advances healthcare solutions and patient outcomes. Discover more about our research capabilities and start a conversation with our team today.
ENABLING MATERIALS FOR CUTTING-EDGE APPLICATIONS
Explore Our Work in Action
Discover how AMAZEMET supports research and innovation through real-world collaborations and deep technical insights
Case Studies
Our case studies showcase how we’ve supported partners across industries with tailored solutions—from alloy development to process optimization. They focus on real challenges and how our technology helped turn ideas into results.
Application Notes
Application notes provide a deeper look into the technical aspects of our systems, methods, and materials. They’re ideal for researchers and engineers seeking detailed knowledge and insights to guide their own experiments and development work.
LET’S TALK
Enhance your biomedical solutions and unlock new possibilities in medical innovation
Enhance your biomedical solutions and unlock new possibilities in medical innovation.

Contact us today to get a quote for your customized rePOWDER setup.